Overview
In the realm of medical science, the evolution of surgical techniques has led to groundbreaking innovations aimed at improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Ablation surgery stands as a testament to such advancements, offering hope and relief to individuals battling various health conditions. In this blog, we delve into the intricacies of ablation surgery, shedding light on its mechanisms, applications, and the latest research findings that underscore its effectiveness.
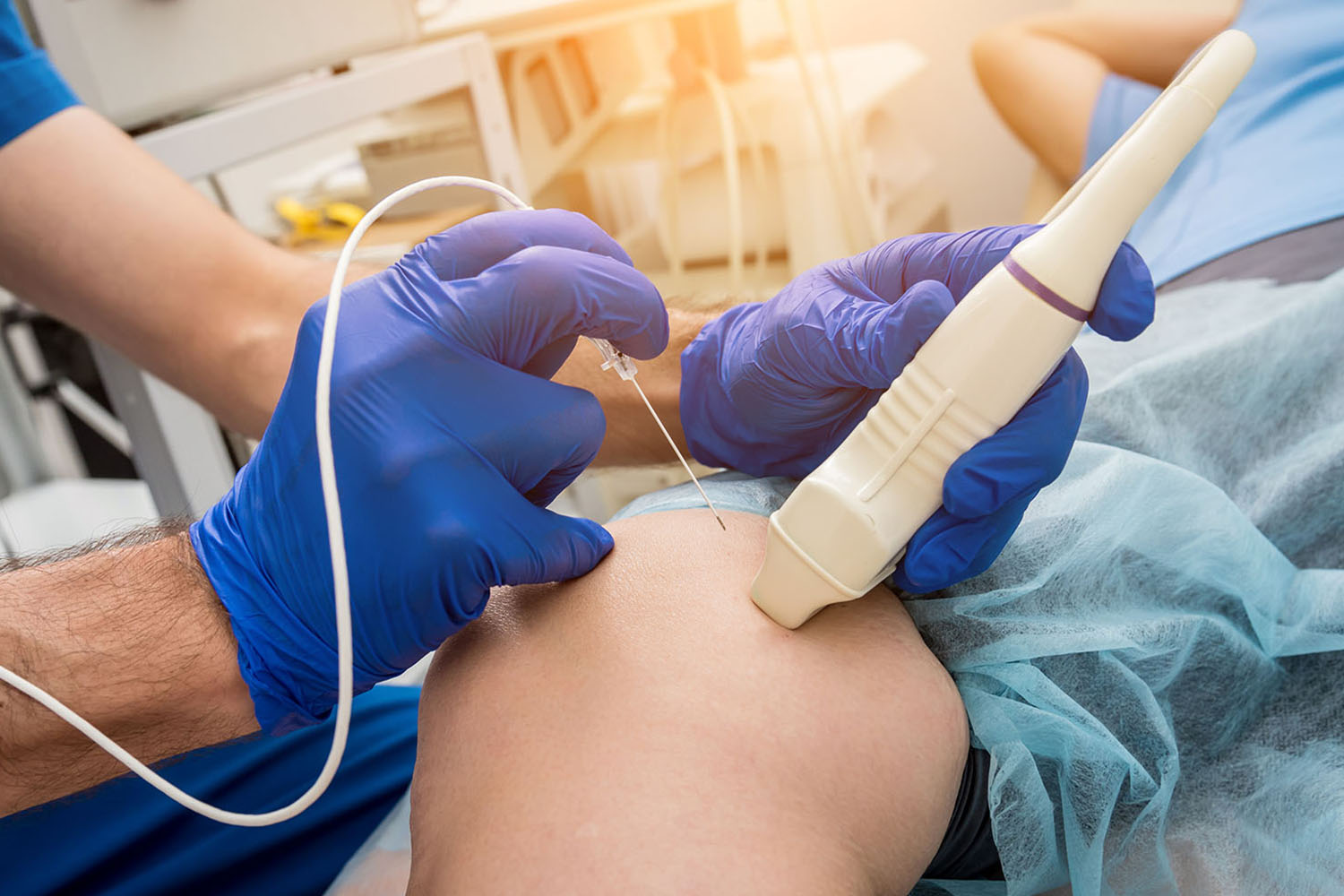
Understanding Ablation Surgery:
Ablation surgery refers to a minimally invasive procedure that involves the targeted destruction of abnormal tissues or cells using various energy sources such as heat, cold, or radiofrequency waves. This technique is employed across diverse medical specialties, including cardiology, oncology, and neurology, to treat conditions ranging from cardiac arrhythmias and tumors to chronic pain syndromes.
The Mechanism Behind Ablation:
The fundamental principle underlying ablation surgery is to disrupt the aberrant cellular activity responsible for causing disease symptoms. By precisely delivering energy to the targeted tissue, ablation induces localized necrosis or elimination of pathological cells, thereby alleviating symptoms and improving patient health. This precise targeting minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissue and mitigates the risk of adverse effects commonly associated with traditional surgical approaches.
Applications Across Medical Specialties:
Ablation surgery has revolutionized the management of various medical conditions, offering patients a less invasive alternative to conventional treatments. In cardiology, it is utilized to correct cardiac arrhythmias by ablating the abnormal electrical pathways responsible for irregular heart rhythms. In oncology, ablation techniques such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA) are employed for the localized destruction of tumors, offering a viable option for patients who are not candidates for surgery or who seek a less invasive treatment modality. Moreover, in the field of pain management, ablative procedures such as radiofrequency ablation of nerves provide long-lasting relief for individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions like arthritis or sciatica.
Evidenced-Based Research Supporting Efficacy:
A wealth of research studies has demonstrated the efficacy and safety of ablation surgery across various medical applications. For instance, a systematic review published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology highlighted the effectiveness of catheter ablation in treating atrial fibrillation, with favorable outcomes in terms of rhythm control and symptom relief. Similarly, studies investigating the use of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common type of liver cancer, have reported high rates of tumor eradication and improved survival rates in select patient populations.
Future Directions and Considerations:
As technology continues to advance, the landscape of ablation surgery is poised for further innovation and refinement. Ongoing research endeavors aim to enhance the precision and efficacy of ablative techniques while minimizing procedural risks and optimizing patient outcomes. Moreover, the integration of imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound guidance facilitates real-time visualization and accurate targeting during ablation procedures, further enhancing their safety and efficacy.
Ablation surgery represents a transformative approach to managing a myriad of medical conditions, offering patients a minimally invasive alternative with favorable outcomes. Through a combination of cutting-edge technology and evidence-based practice, ablation techniques continue to redefine the standard of care across various medical specialties, ushering in a new era of precision medicine.



