Overview
Angiography is a crucial diagnostic and therapeutic tool in modern medicine, enabling doctors to visualize the inside of blood vessels and organs, particularly the arteries, veins, and heart chambers. This technique plays a vital role in diagnosing and managing a variety of cardiovascular conditions. Leveraging international research, this blog delves into the importance, procedure, and advancements in angiography, shedding light on its global impact.
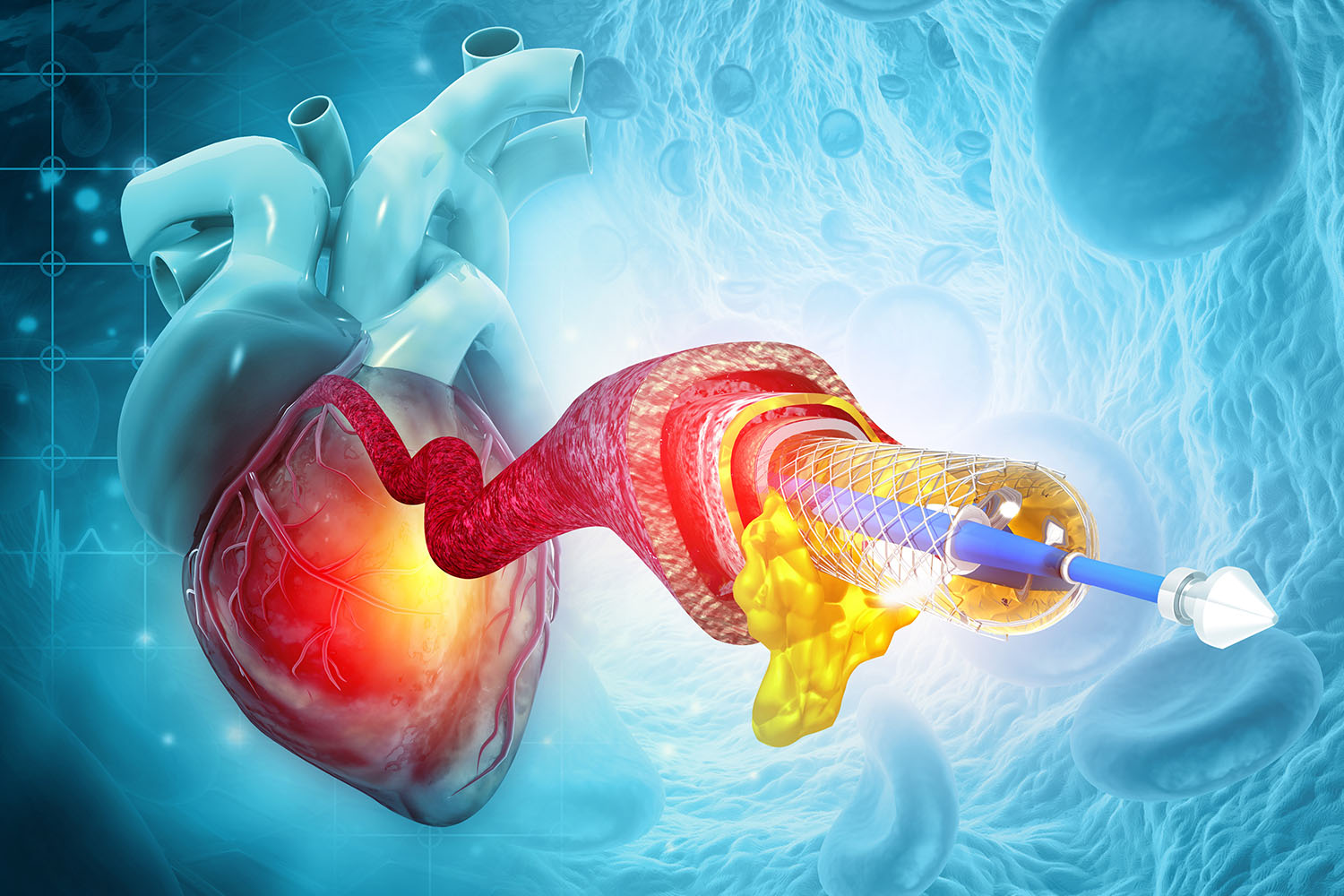
What is Angiography?
Angiography, also known as arteriography, is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the interior of blood vessels and organs of the body, with a particular focus on the arteries, veins, and heart chambers. The procedure involves the injection of a contrast dye into the bloodstream, which makes the blood vessels visible on X-ray, CT (computed tomography), or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans.
The Procedure
The angiography procedure typically involves the following steps:
Preparation: The patient may need to fast for several hours before the procedure. A mild sedative is often administered to help the patient relax.
Insertion of Catheter: A small incision is made, usually in the groin, wrist, or arm, and a thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into the blood vessel.
Injection of Contrast Dye: The catheter is guided to the area of interest, and a contrast dye is injected through it. This dye helps to highlight the blood vessels on the imaging scans.
Imaging: As the dye flows through the blood vessels, images are taken using X-ray, CT, or MRI. These images help doctors identify blockages, abnormalities, or other issues within the vessels.
Completion: Once the necessary images are obtained, the catheter is removed, and the incision site is closed. Patients typically need to rest for a few hours to prevent bleeding from the insertion site.
Importance and Applications
Angiography is indispensable for diagnosing and treating various cardiovascular conditions. Some of its key applications include:
Detecting Blockages: It helps in identifying blockages or narrowing of the arteries (stenosis), which can lead to heart attacks or strokes.
Aneurysms: Angiography is used to detect aneurysms, which are abnormal bulges in the blood vessels that can rupture and cause life-threatening bleeding.
Evaluating Blood Flow: It assesses blood flow in different parts of the body, which is crucial for planning surgeries or other interventions.
Guiding Treatments: The procedure can also guide treatments such as angioplasty (widening of narrowed arteries) and stent placement (inserting a small mesh tube to keep the artery open).
Advancements in Angiography
International research has driven significant advancements in angiography, improving its safety, accuracy, and effectiveness. Some notable innovations include:
Non-Invasive Techniques: Advances in CT and MRI angiography have led to the development of non-invasive methods that do not require catheter insertion, reducing the risk of complications.
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA): This technique enhances the clarity of images by subtracting pre-contrast images from post-contrast images, allowing for more precise diagnosis.
3D Angiography: The development of 3D imaging provides a more detailed view of the blood vessels, aiding in better treatment planning and outcomes.
Global Impact
The importance of angiography is underscored by its widespread use across the globe. For instance, according to a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the use of coronary angiography in Europe has significantly increased over the past two decades, contributing to a marked decline in cardiovascular mortality rates . Similarly, in Asia, the adoption of advanced angiographic techniques has improved the management of coronary artery disease, as reported by the Asian Cardiovascular & Thoracic Annals .
Angiography remains a cornerstone of modern diagnostic and interventional cardiology. Its ability to provide detailed images of the blood vessels and guide life-saving treatments makes it an invaluable tool in the fight against cardiovascular diseases. As international research continues to drive technological advancements, the future of angiography promises even greater precision, safety, and accessibility, ensuring better health outcomes for patients worldwide.
Whether it’s detecting life-threatening blockages or guiding intricate surgical procedures, angiography stands as a testament to the remarkable progress in medical imaging technology. By staying abreast of the latest developments and leveraging global expertise, healthcare providers can continue to harness the full potential of angiography in their ongoing efforts to improve cardiovascular health.



