Overview
In the realm of respiratory medicine, bronchoscopy stands as a pivotal diagnostic and therapeutic tool, offering clinicians unparalleled access to the intricate landscape of the lungs and airways. Through advanced imaging techniques and minimally invasive procedures, bronchoscopy plays a vital role in the evaluation and management of various pulmonary conditions. In this blog, we embark on a journey to explore the intricacies of bronchoscopy, drawing upon factual insights and research findings to illuminate its principles, applications, and significance in modern healthcare.
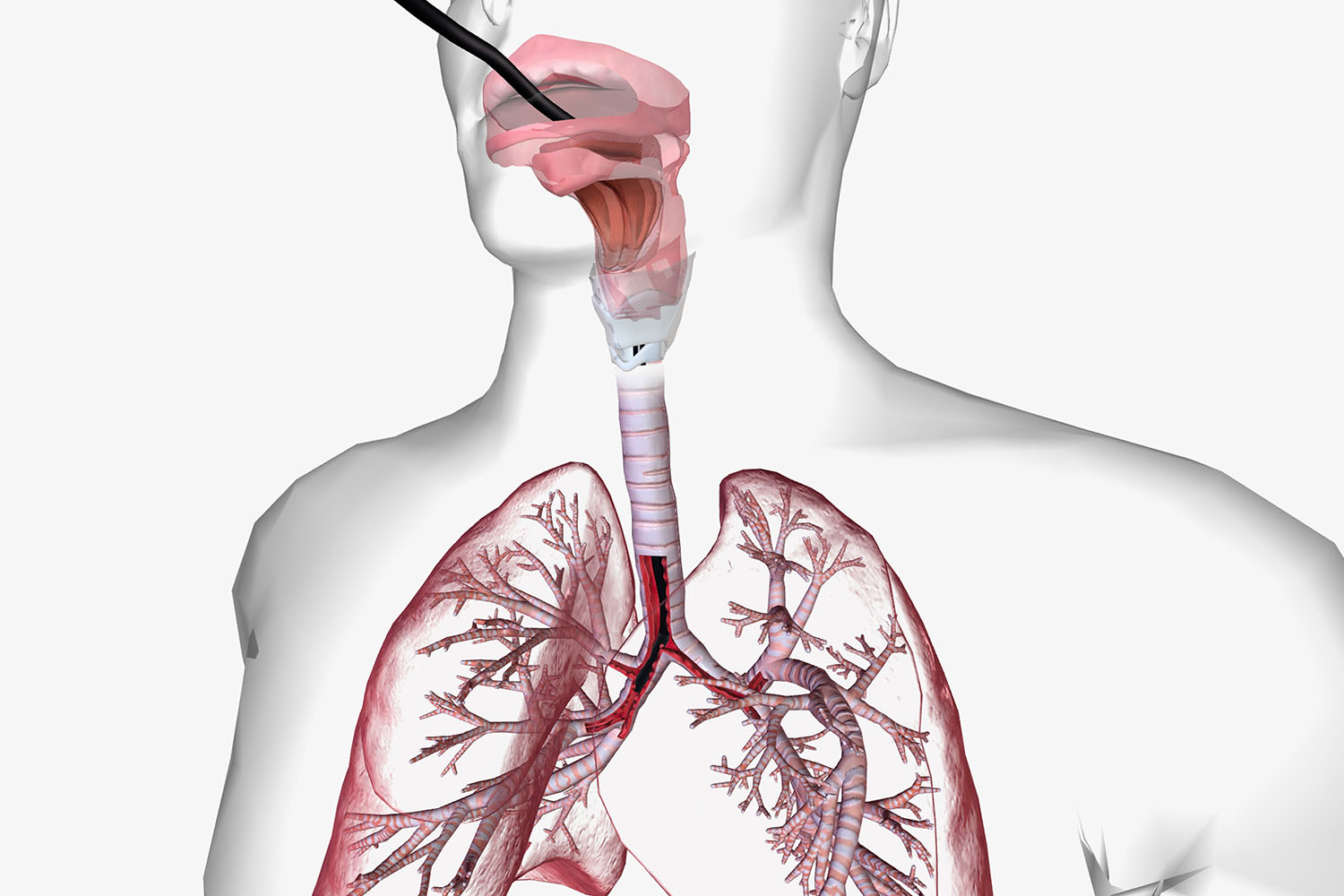
Understanding Bronchoscopy:
Bronchoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube called a bronchoscope into the airways to visualize and assess the lungs, bronchi, and trachea. This versatile tool allows healthcare providers to obtain diagnostic samples, perform therapeutic interventions, and investigate a wide array of pulmonary conditions, ranging from infectious diseases and malignancies to structural abnormalities and airway disorders.
Principles of Bronchoscopy:
Bronchoscopy is typically performed using either a flexible bronchoscope or a rigid bronchoscope, depending on the clinical indication and anatomical considerations. The bronchoscope is equipped with a light source, camera, and working channel, allowing for direct visualization of the airways and instrumentation of biopsy tools, brushes, forceps, and suction devices. Under sedation or general anesthesia, the bronchoscope is advanced through the nose or mouth and guided into the airways, enabling real-time assessment of airway anatomy, secretions, and lesions.
Applications of Bronchoscopy:
Bronchoscopy serves a myriad of diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in the evaluation and management of respiratory conditions, including:
- Diagnostic Bronchoscopy: Bronchoscopy allows for direct visualization and sampling of the airway mucosa, facilitating the diagnosis of conditions such as lung cancer, pneumonia, tuberculosis, interstitial lung disease, and airway infections.
- Therapeutic Bronchoscopy: Bronchoscopy enables a range of therapeutic interventions, including bronchial biopsies, bronchial brushing, bronchoalveolar lavage, endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS), transbronchial needle aspiration (TBNA), bronchial stenting, laser therapy, cryotherapy, and endobronchial tumor debulking.
- Interventional Bronchoscopy: Interventional bronchoscopy techniques, such as navigational bronchoscopy and electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy (ENB), allow for precise localization of pulmonary lesions and targeted biopsy or ablation of peripheral lung nodules.
Significance of Bronchoscopy:
Bronchoscopy plays a crucial role in the diagnosis, staging, and management of a wide range of pulmonary conditions, offering clinicians valuable insights into airway anatomy, pathology, and physiology. Research has demonstrated the efficacy and safety of bronchoscopy in guiding treatment decisions, improving diagnostic accuracy, and facilitating minimally invasive interventions for lung cancer, infectious diseases, and airway disorders. As technology continues to advance, bronchoscopy remains at the forefront of respiratory care, driving innovation and optimizing patient outcomes in the quest for respiratory health and well-being.
Bronchoscopy stands as a cornerstone in the diagnostic and therapeutic armamentarium of respiratory medicine, offering clinicians a window into the inner workings of the lungs and airways. Through its versatility, precision, and minimally invasive approach, bronchoscopy empowers healthcare providers to navigate the depths of respiratory health with confidence and expertise. As we continue to unlock the mysteries of pulmonary disease and innovation, let us embrace the transformative potential of bronchoscopy in shaping the landscape of respiratory care and improving the lives of patients worldwide.



