Overview
Bursitis in the hip is a common orthopedic condition that affects individuals of all ages, causing pain and discomfort in the hip joint. While often considered a localized issue, bursitis in the hip can have a significant impact on daily activities and quality of life. By delving into international research and clinical findings, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of this condition and explore effective management strategies.
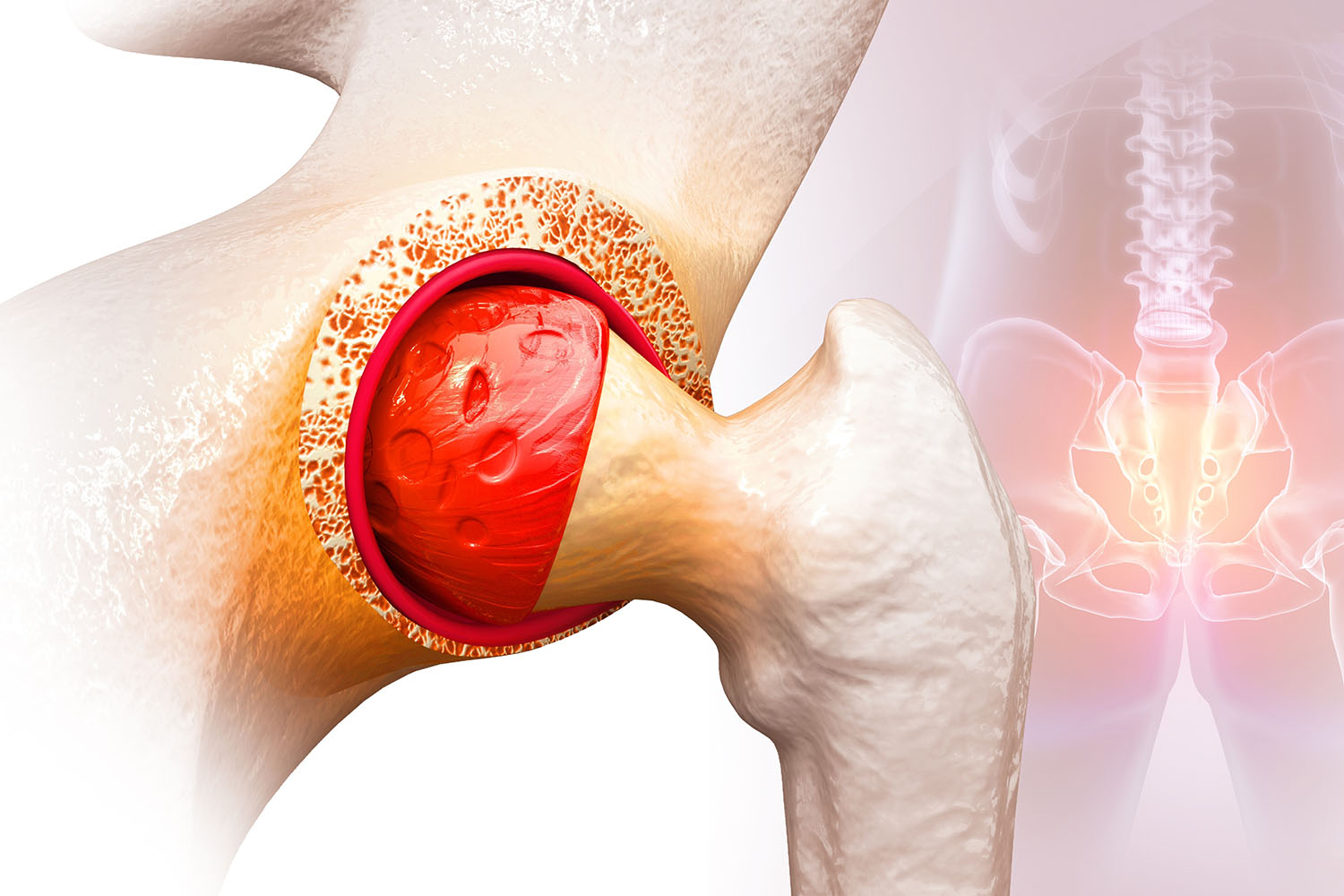
Bursitis refers to the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions between bones, tendons, and muscles, reducing friction and allowing smooth movement of joints. In the hip, several bursae facilitate movement and provide support, with the trochanteric bursa being the most commonly affected in hip bursitis.
Research indicates that bursitis in the hip can result from various factors, including repetitive motions, overuse injuries, trauma, or underlying conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, anatomical abnormalities or biomechanical issues may predispose individuals to develop hip bursitis.
The hallmark symptom of hip bursitis is pain, typically located on the outside of the hip and may radiate down the thigh. Pain worsens with activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or prolonged periods of standing, and may be accompanied by swelling and tenderness in the affected area. In some cases, individuals may experience stiffness and limited range of motion in the hip joint.
International research emphasizes the importance of accurate diagnosis in guiding appropriate management strategies for hip bursitis. Healthcare providers often utilize a combination of clinical assessment, imaging studies such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and diagnostic injections to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of hip pain.
Once diagnosed, the management of hip bursitis focuses on alleviating pain, reducing inflammation, and restoring function. Non-surgical approaches, including rest, activity modification, ice therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and physical therapy, form the cornerstone of treatment for most individuals with hip bursitis.
In cases where conservative measures fail to provide relief, or if bursitis becomes chronic or recurrent, interventional treatments such as corticosteroid injections or ultrasound-guided needle aspiration of the bursa may be considered. These procedures aim to reduce inflammation and provide symptomatic relief, allowing individuals to resume their daily activities with minimal discomfort.
It’s essential to recognize that while hip bursitis can be debilitating, proactive management and lifestyle modifications can help prevent recurrence and promote long-term joint health. Engaging in regular low-impact exercises, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms are key components of a comprehensive approach to managing hip bursitis.
Bursitis in the hip is a prevalent condition characterized by inflammation of the bursae surrounding the hip joint. Through a combination of international research findings and evidence-based interventions, healthcare providers can effectively diagnose and manage hip bursitis, empowering individuals to regain function and improve their quality of life. By raising awareness and promoting early intervention, we can ensure timely access to treatment and support for those affected by hip bursitis.



