Overview
Carotid artery disease, a leading cause of stroke, has prompted extensive research and the development of advanced medical procedures to prevent such debilitating events. Among these procedures, Carotid Artery Revascularization stands out as a critical intervention for restoring proper blood flow to the brain. This blog delves into the significance, methods, and global research on Carotid Artery Revascularization.
What is Carotid Artery Revascularization?
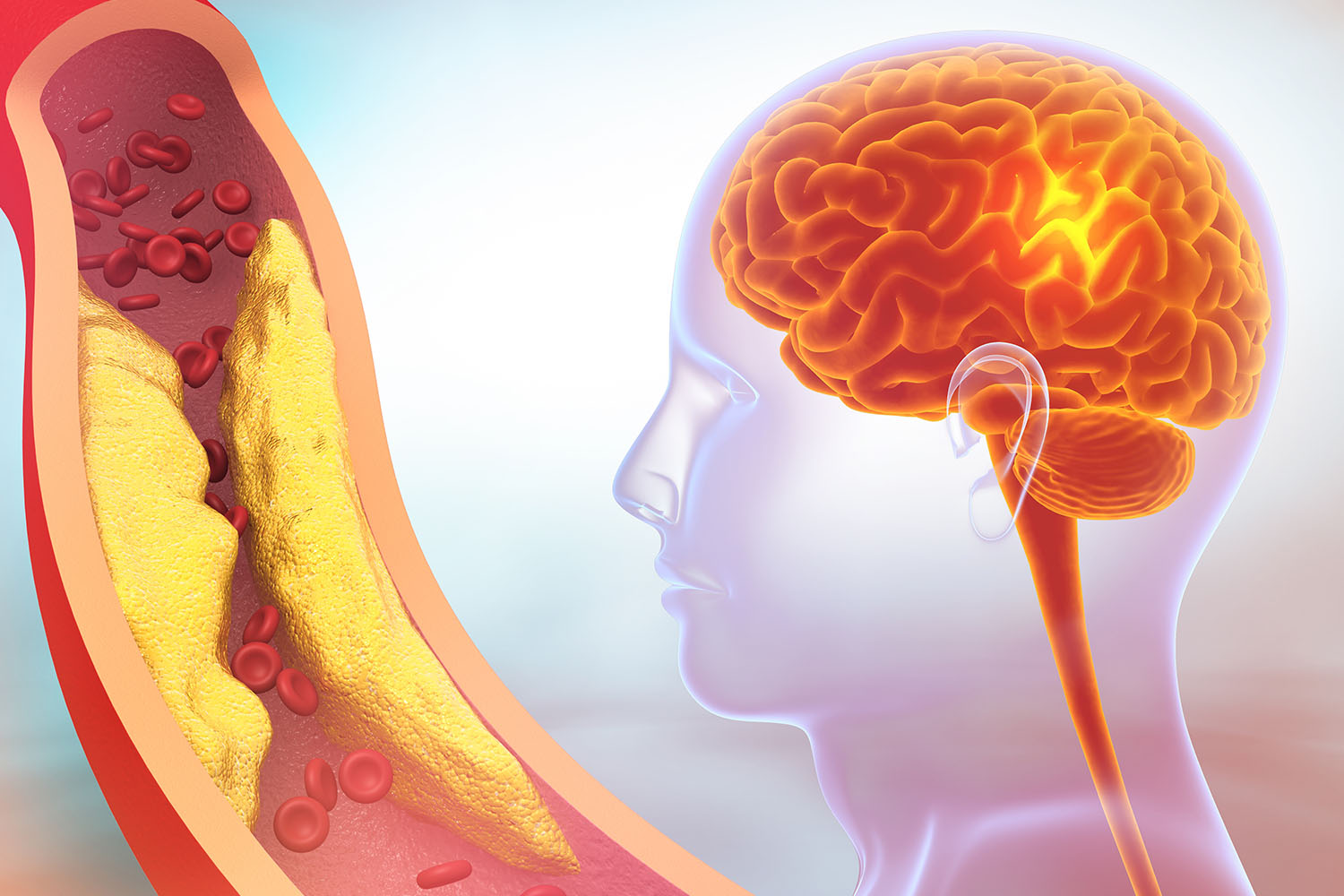
Carotid Artery Revascularization refers to the medical procedures aimed at restoring adequate blood flow through the carotid arteries, which are vital blood vessels located on each side of the neck. These arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain. When these arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis), the risk of stroke significantly increases.
Importance of Carotid Artery Revascularization
Stroke is a leading cause of death and long-term disability worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 15 million people suffer from strokes annually, and nearly 5 million of these cases result in death. Effective management of carotid artery disease through revascularization can dramatically reduce the incidence of stroke, potentially saving lives and improving the quality of life for many individuals.
Methods of Carotid Artery Revascularization
There are primarily two methods of Carotid Artery Revascularization:
- Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA): This surgical procedure involves the removal of plaque from the carotid artery. A surgeon makes an incision in the neck to access the artery, removes the plaque, and then stitches the artery closed. This procedure has been the gold standard for many years due to its effectiveness in reducing the risk of stroke.
- Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS): This minimally invasive procedure involves the insertion of a stent (a small mesh tube) into the carotid artery to keep it open. A catheter is threaded through a blood vessel to the site of the blockage, where a balloon is inflated to expand the artery. The stent is then placed to keep the artery open, ensuring adequate blood flow to the brain.
International Research and Findings
Global research has continuously evolved to improve the outcomes of Carotid Artery Revascularization. Here are some key findings from recent studies:
- Comparison of CEA and CAS: A comprehensive study published in The Lancet (2020) compared the long-term outcomes of CEA and CAS. The study found that while both procedures are effective, CEA had a slightly lower risk of stroke in the perioperative period compared to CAS. However, CAS was associated with fewer complications related to the surgical site.
- Advancements in Stent Technology: Research from the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2021) highlighted significant advancements in stent technology, leading to improved safety and efficacy of CAS. Newer stents with enhanced flexibility and drug-eluting properties have shown promising results in reducing restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery).
- Patient Selection and Personalized Treatment: A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019) emphasized the importance of personalized treatment plans. Factors such as age, comorbidities, and anatomical considerations play a crucial role in determining the most suitable revascularization method for each patient. This approach ensures optimal outcomes and minimizes risks.
- Global Guidelines and Recommendations: The European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) and the American Heart Association (AHA) have developed guidelines for the management of carotid artery disease. These guidelines recommend Carotid Artery Revascularization for patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis (narrowing) of 50-99% and asymptomatic stenosis of 60-99%, especially when life expectancy exceeds 3-5 years.
Future Directions
The field of Carotid Artery Revascularization continues to evolve with ongoing research and technological advancements. Future directions include:
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: The integration of robotics in CEA is being explored to enhance precision and reduce recovery times.
- Biodegradable Stents: Research is underway to develop stents that gradually dissolve over time, reducing the long-term risk of complications.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being utilized to improve patient selection, predict outcomes, and personalize treatment plans based on vast datasets.
Carotid Artery Revascularization remains a cornerstone in the prevention of stroke, offering hope and improved quality of life to millions of patients worldwide. With ongoing research and technological advancements, the future of this critical intervention looks promising, paving the way for safer, more effective treatments. It is essential for patients to have informed discussions with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate revascularization method tailored to their specific needs.
By staying abreast of the latest research and adhering to international guidelines, healthcare professionals can continue to make significant strides in the fight against stroke and carotid artery disease.