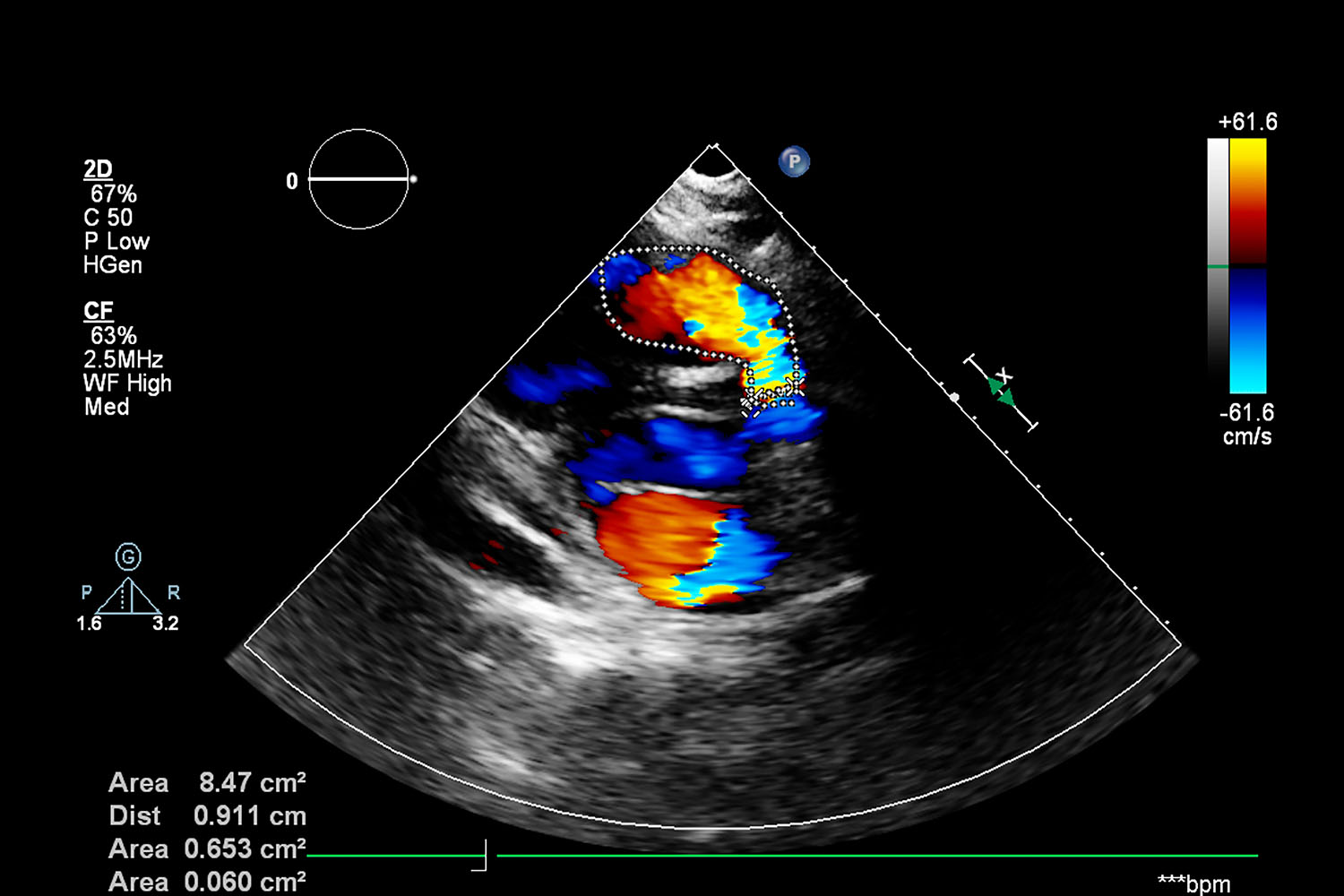
Overview
In the realm of medical diagnostics, few technologies have had as profound an impact as the ECHO. But what exactly does “ECHO” stand for? The full form of ECHO is “Echocardiography,” a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart. This technology has revolutionized the way cardiologists diagnose and manage heart conditions, making it an indispensable tool in modern medicine.
The Basics of Echocardiography
Echocardiography, commonly referred to as an ECHO, involves the use of high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the heart’s structure and function. By placing a transducer on the patient’s chest, doctors can capture real-time images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow. This allows for a comprehensive assessment of cardiac health without the need for invasive procedures.
The Evolution of ECHO
The development of echocardiography dates back to the 1950s when Swedish cardiologist Inge Edler, along with physicist Carl Hellmuth Hertz, pioneered the use of ultrasound in cardiology. Their groundbreaking work laid the foundation for the advanced echocardiographic techniques used today. Over the decades, echocardiography has evolved, incorporating advancements such as Doppler imaging, 3D echocardiography, and strain imaging, further enhancing its diagnostic capabilities.
Global Research and Advances
International research continues to expand the potential of echocardiography. Recent studies have focused on the use of contrast echocardiography, which involves injecting a contrast agent to improve image clarity, especially in patients with suboptimal echocardiographic windows. This technique has proven valuable in diagnosing conditions such as coronary artery disease and heart failure.
Moreover, research in strain imaging, a sophisticated echocardiographic method that assesses myocardial deformation, has shown promise in early detection of cardiac dysfunction in patients undergoing chemotherapy or those with diabetes. These advancements underscore the global efforts to refine echocardiographic techniques and improve patient outcomes.
Applications of Echocardiography
Echocardiography plays a crucial role in diagnosing a wide range of heart conditions, including:
- Congenital Heart Disease: ECHO is essential in detecting structural abnormalities in newborns and children.
- Heart Failure: It helps evaluate the heart’s pumping efficiency and guides treatment decisions.
- Valvular Heart Disease: ECHO assesses the function and structure of heart valves, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions like stenosis and regurgitation.
- Cardiomyopathy: ECHO provides insights into the heart muscle’s condition, helping diagnose diseases that affect the myocardium.
The Future of ECHO
As technology advances, the future of echocardiography looks promising. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in echocardiographic analysis is set to revolutionize the field. AI algorithms can assist in interpreting complex echocardiographic data, reducing variability and increasing diagnostic accuracy. Additionally, portable and handheld echocardiographic devices are making this technology more accessible, especially in remote and underserved areas.
The full form of ECHO, “Echocardiography,” represents more than just a medical term; it signifies a critical tool in cardiology that has transformed patient care worldwide. Through continuous research and technological advancements, echocardiography remains at the forefront of cardiac diagnostics, offering hope and improved outcomes for patients with heart disease. As we look to the future, the global medical community continues to build on this foundation, striving to enhance the capabilities and accessibility of this indispensable diagnostic tool.