Overview
In the realm of cardiovascular medicine, echocardiography stands as a cornerstone diagnostic tool, offering unparalleled insights into the structure and function of the heart. This non-invasive imaging technique utilizes sound waves to create detailed images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and surrounding structures, providing invaluable information for the diagnosis and management of various cardiac conditions. Let’s embark on a journey into the world of echocardiography, uncovering its capabilities, applications, and the latest research insights.
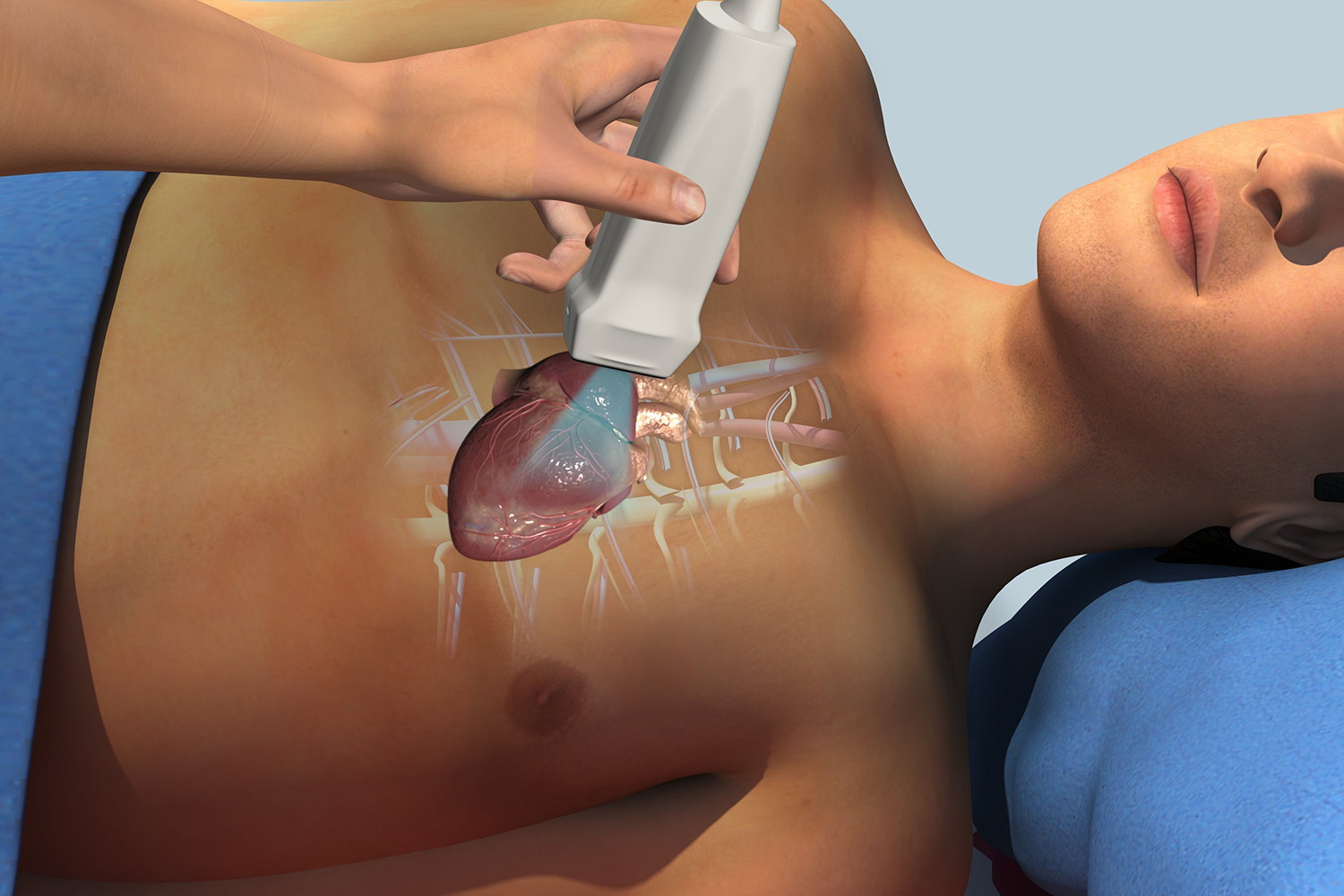
Understanding Echocardiography
Echocardiography, often referred to as an “echo” for short, employs high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to produce real-time images of the heart in motion. By capturing images from different angles and perspectives, echocardiography enables visualization of cardiac structures and blood flow patterns with exceptional clarity and precision.
Types of Echocardiography
There are several types of echocardiography, each serving specific diagnostic purposes:
1. Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE): This is the most common type of echocardiography, performed by placing a transducer on the chest wall to obtain images of the heart from the outside of the body.
2. Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE): In this procedure, a specialized transducer is inserted into the esophagus to obtain detailed images of the heart from within the body. TEE offers superior visualization of cardiac structures, particularly the posterior regions of the heart.
3. Stress Echocardiography: This test involves performing echocardiography before and after exercise or pharmacological stress to assess cardiac function and detect ischemia (reduced blood flow to the heart muscle).
4. Three-Dimensional (3D) Echocardiography: Utilizing advanced imaging technology, 3D echocardiography provides detailed three-dimensional images of the heart, allowing for comprehensive assessment of cardiac anatomy and function.
Applications in Clinical Practice
Echocardiography plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of a wide range of cardiac conditions, including:
Valvular heart disease: Echocardiography can assess the structure and function of heart valves, detecting abnormalities such as stenosis (narrowing) or regurgitation (leakage).
Cardiomyopathy: Echocardiography helps evaluate the size, shape, and function of the heart muscle, aiding in the diagnosis and classification of various types of cardiomyopathy.
Congenital heart defects: Echocardiography enables visualization of structural abnormalities present from birth, facilitating early detection and intervention in pediatric and adult patients.
Heart failure: Echocardiography provides essential information about cardiac function, chamber dimensions, and ejection fraction, guiding treatment decisions and monitoring disease progression.
Research Insights and Advancements
Advancements in echocardiography technology and research methodologies continue to expand the capabilities and applications of this indispensable imaging modality. Research studies published in leading cardiovascular journals such as Circulation and Journal of the American College of Cardiology have explored novel echocardiographic techniques, including strain imaging, speckle tracking, and contrast-enhanced imaging, for the assessment of myocardial mechanics and perfusion.
Furthermore, emerging research focuses on the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of echocardiographic interpretation. Studies investigating AI-based image analysis algorithms for automated detection of cardiac abnormalities hold promise for improving diagnostic accuracy and streamlining clinical workflow.



