Overview
Electromyography (EMG) testing is a valuable diagnostic tool utilized by healthcare professionals to assess the health and function of muscles and the nerves controlling them. In this blog, we delve into the intricacies of EMG testing, exploring its uses, procedures, and the wealth of scientific research backing its efficacy.
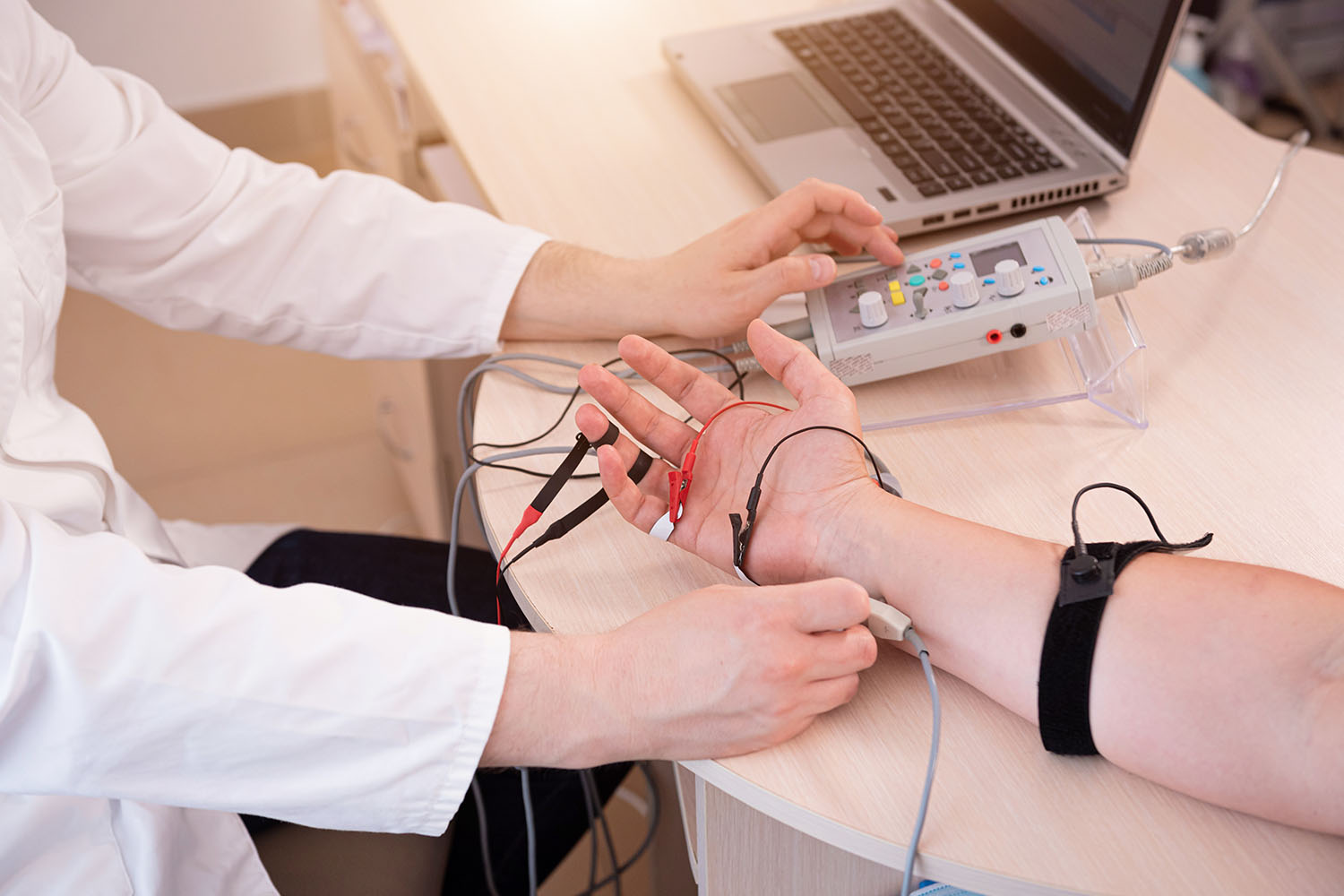
Understanding EMG Testing:
EMG testing involves measuring and recording electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles at rest and during contraction. This non-invasive procedure provides valuable insights into muscle and nerve function, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various neuromuscular disorders.
Applications of EMG Testing:
EMG testing serves a multitude of clinical purposes, including:
Diagnosis of Neuromuscular Disorders: EMG testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing conditions such as peripheral neuropathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, myasthenia gravis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), among others.
Assessment of Nerve Damage: By evaluating the electrical activity of muscles, EMG testing can identify nerve damage or dysfunction, aiding in the localization and characterization of nerve injuries.
Monitoring Disease Progression: EMG testing can track changes in muscle and nerve function over time, enabling healthcare providers to monitor disease progression and tailor treatment strategies accordingly.
The EMG Procedure:
During an EMG procedure, a small, thin needle electrode is inserted into specific muscles under sterile conditions. The electrode records the electrical signals generated by muscle activity, which are displayed as waveforms on a monitor or captured digitally for analysis. Additionally, nerve conduction studies (NCS) may be performed concurrently to assess the speed and efficiency of nerve impulses.
Scientific Evidence and Research:
A wealth of scientific research supports the efficacy and utility of EMG testing in clinical practice:
Diagnostic Accuracy: Studies have demonstrated the high diagnostic accuracy of EMG testing in identifying neuromuscular disorders and distinguishing between different pathologies affecting muscles and nerves.
Treatment Guidance: Research indicates that EMG testing results can inform treatment decisions, such as determining the appropriate course of therapy for conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or guiding surgical interventions in cases of nerve compression.
Prognostic Value: EMG findings have prognostic significance in certain neuromuscular disorders, helping clinicians predict disease progression and long-term outcomes for patients.



