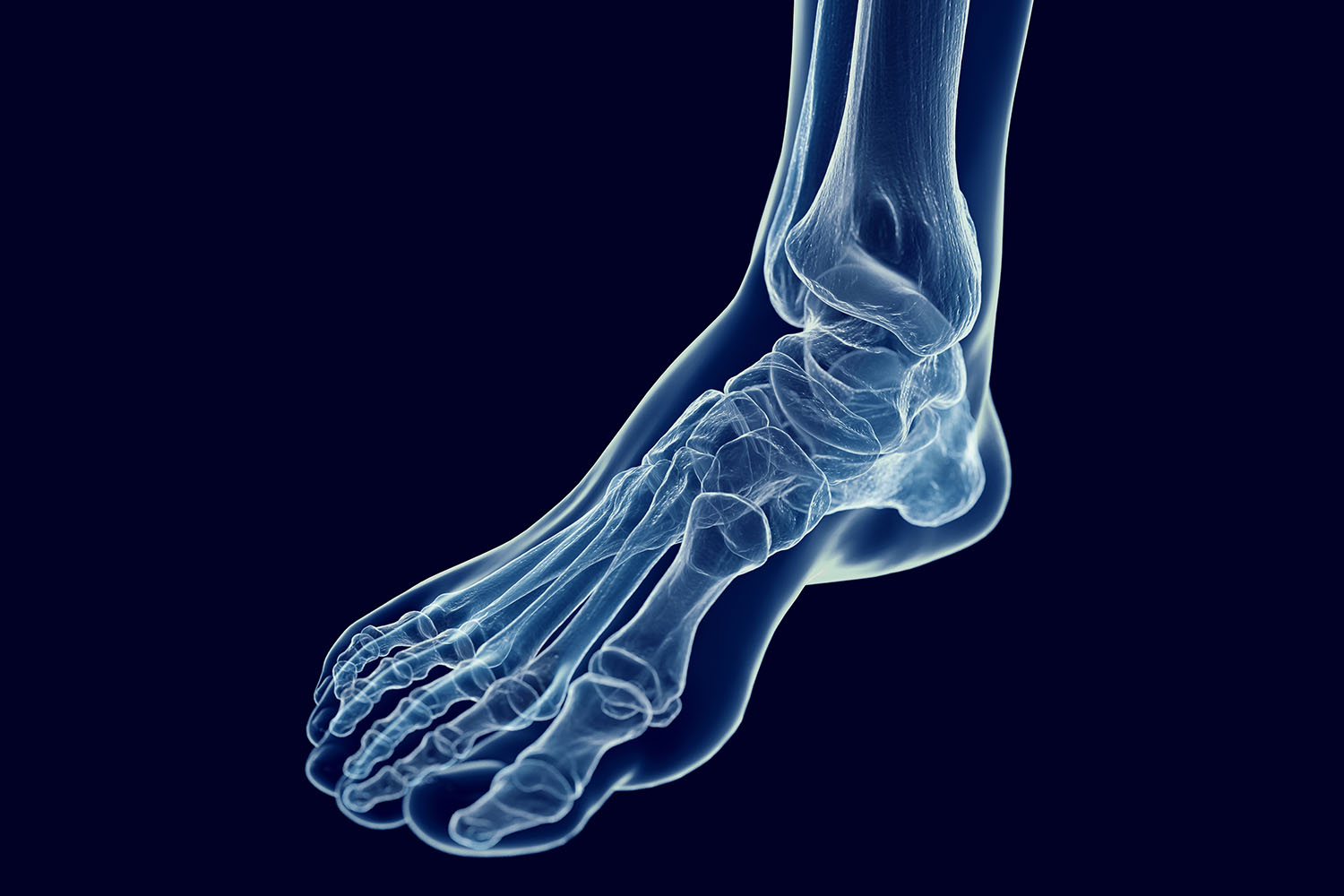
Overview
Understanding the foot bone anatomy is crucial for anyone interested in human biology, sports medicine, or podiatry. The foot is a complex structure composed of bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments, all working together to provide support, balance, and mobility. This blog will delve into the intricacies of foot bone anatomy, backed by international research, to provide a detailed overview of this fascinating topic.
The Structure of the Foot
The human foot consists of 26 bones, which can be categorized into three main groups:
- Tarsal Bones
- Metatarsal Bones
- Phalanges
Tarsal Bones
The tarsal bones are located in the hindfoot and midfoot. They are crucial for weight-bearing and movement. There are seven tarsal bones:
- Calcaneus: Known as the heel bone, it is the largest tarsal bone and provides the foundation for the rear part of the foot.
- Talus: This bone sits above the calcaneus and forms the lower part of the ankle joint.
- Navicular: Located in front of the talus, it plays a role in maintaining the arch of the foot.
- Cuboid: Positioned on the lateral side of the foot, it works with the calcaneus to provide stability.
- Cuneiforms: There are three cuneiform bones (medial, intermediate, and lateral) located between the navicular and the first three metatarsals.
Metatarsal Bones
The metatarsal bones are five long bones that connect the tarsal bones to the phalanges. They are numbered from one to five, starting from the medial side (big toe) to the lateral side (little toe). These bones play a crucial role in providing support and balance during walking and running.
Phalanges
The phalanges are the bones of the toes. Each toe has three phalanges (proximal, middle, and distal), except for the big toe, which has only two (proximal and distal). The phalanges are essential for the movement and stability of the toes.
The Role of Foot Bones in Movement
The foot bones work in harmony with the muscles, tendons, and ligaments to facilitate movement and provide support. The arches of the foot, formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, act as shock absorbers and help distribute weight evenly across the foot. This intricate arrangement allows for efficient walking, running, and jumping.
Common Foot Bone Disorders
Understanding foot bone anatomy helps in diagnosing and treating various foot disorders. Some common conditions include:
- Plantar Fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, often caused by overuse or improper footwear.
- Bunions: A bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of the big toe, often due to genetic factors or ill-fitting shoes.
- Fractures: Stress fractures are common in athletes and can occur in any of the foot bones, particularly the metatarsals.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the joints in the foot, leading to pain and stiffness.
International Research on Foot Bone Anatomy
Research on foot bone anatomy is continuously evolving, with studies conducted worldwide to better understand foot mechanics and pathology. A study published in the Journal of Foot and Ankle Research highlighted the importance of foot bone structure in diagnosing and treating flatfoot deformities. Another research article from the International Journal of Sports Medicine explored the impact of different types of footwear on foot bone stress and injury prevention.
Advancements in imaging technologies, such as MRI and CT scans, have significantly improved our ability to study foot bone anatomy in detail. These tools allow for precise diagnosis of fractures, deformities, and other conditions, leading to more effective treatments.
Conclusion
Foot bone anatomy is a complex and fascinating area of study that plays a vital role in our daily lives. From providing support and balance to enabling movement, the bones of the foot are essential components of human anatomy. Understanding their structure and function is crucial for diagnosing and treating various foot disorders. Continuous research and advancements in medical technology are enhancing our knowledge and ability to care for our feet.
By exploring foot bone anatomy, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate design of the human body and the importance of maintaining foot health.