Overview
In the intricate realm of cardiac medicine, innovations continually push the boundaries of what’s possible, offering renewed hope to patients battling arrhythmias and other heart rhythm disorders. Among these advancements, heart ablation surgery emerges as a transformative intervention, wielding precision and efficacy in restoring normal heart rhythm. Let’s delve into the depths of ablation surgery, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and the research driving its evolution.
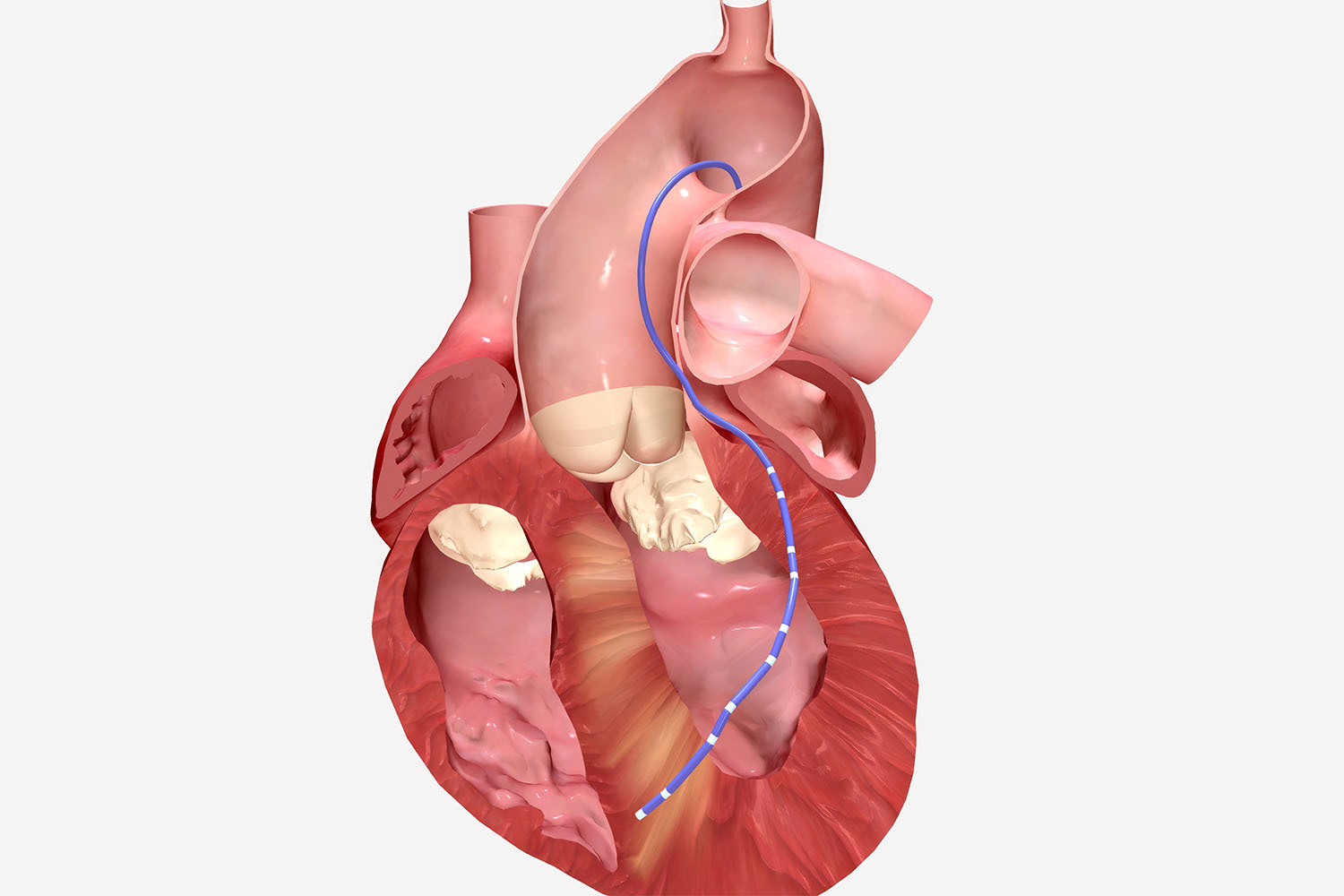
Heart Ablation surgery
Heart Ablation surgery : The very term resonates with promise, signifying a targeted approach to treating irregular heart rhythms. But what exactly is ablation surgery, and how does it work? At its essence, ablation involves the strategic destruction of abnormal cardiac tissue responsible for generating erratic electrical signals. This is achieved through the delivery of radiofrequency or cryothermal energy via catheters inserted into the heart, effectively creating scars that disrupt the aberrant electrical pathways.
Research into ablation surgery has yielded compelling evidence of its efficacy in restoring normal heart rhythm and improving patients’ quality of life. Numerous studies have demonstrated high success rates in eliminating arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and atrial flutter. Furthermore, advancements in mapping technologies and catheter design have enhanced the precision and safety of ablation procedures, minimizing the risk of complications and optimizing outcomes.
One notable area of research driving the evolution of ablation surgery lies in its application to complex arrhythmias and patient populations previously considered challenging to treat. Studies have shown promising results in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation and structural heart disease, highlighting the expanding role of ablation as a viable treatment option for a broader spectrum of cardiac conditions.
Moreover, the integration of advanced imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and three-dimensional electroanatomic mapping has facilitated more accurate identification and targeting of arrhythmogenic substrates, further enhancing the success rates of ablation procedures.
Beyond its clinical efficacy, ablation surgery offers distinct advantages over pharmacological therapies, particularly in terms of long-term symptom management and reducing the reliance on antiarrhythmic medications with potential side effects. Additionally, the minimally invasive nature of catheter-based ablation translates to shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and improved overall patient satisfaction.
As we stand on the precipice of a new era in cardiac care, ablation surgery shines as a beacon of hope for millions of individuals worldwide grappling with heart rhythm disorders. With ongoing research fueling innovation and refinement, the potential of ablation to transform lives and reshape the landscape of cardiovascular medicine is boundless. In the relentless pursuit of excellence, ablation surgery stands as a testament to the remarkable progress achieved when science, technology, and compassion converge in the service of healing.