Overview
The human heart is a marvel of biological engineering, a powerful organ that tirelessly pumps blood throughout the body, sustaining life. Understanding heart anatomy is crucial for appreciating how this vital organ functions and for advancing medical research and treatment. This blog delves into the intricate details of heart anatomy, drawing on international research to provide a thorough understanding of its structure and operation.
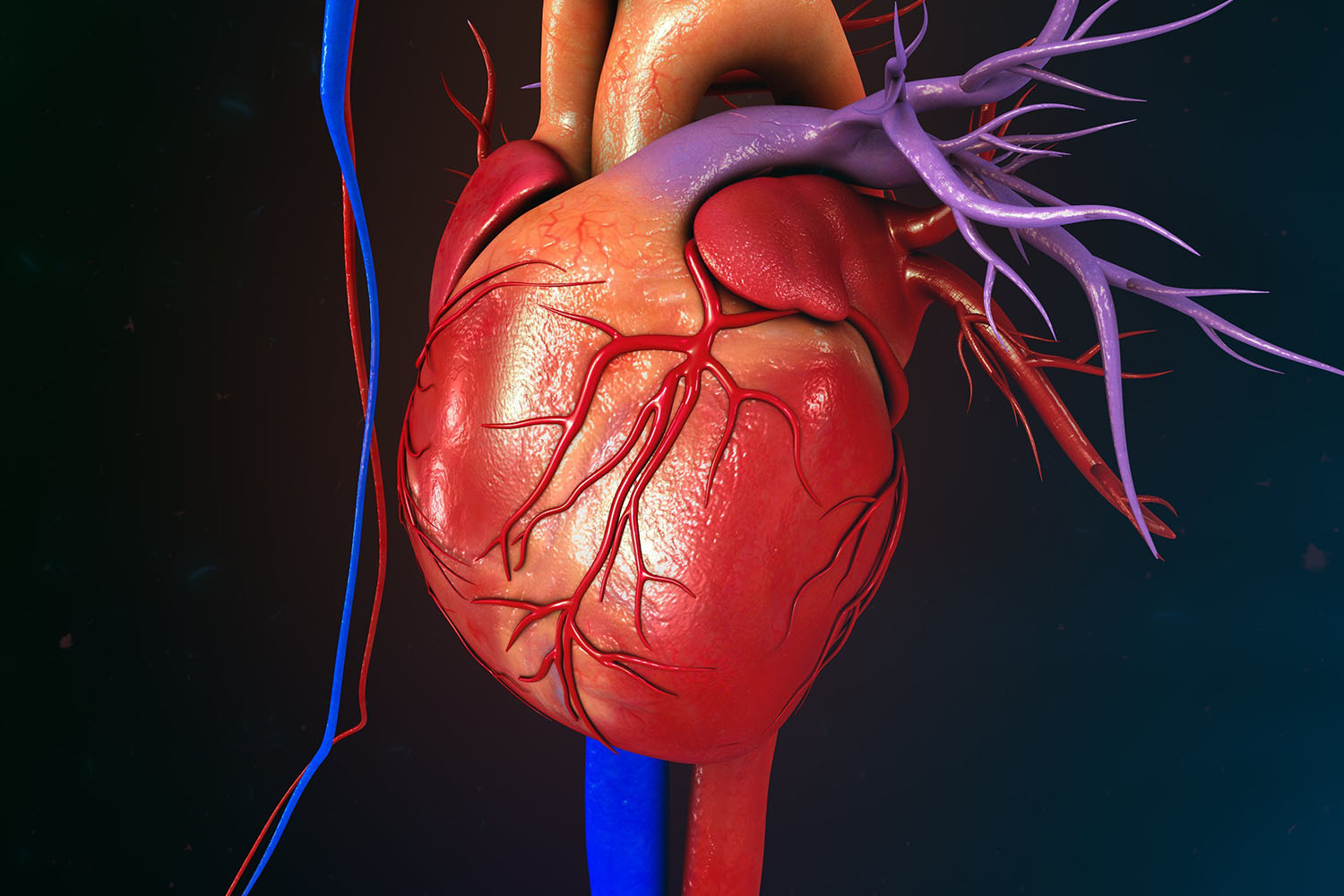
The Structure of the Heart
The heart is a muscular organ about the size of a fist, located slightly to the left of the center of the chest. It is divided into four chambers: two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers). The right side of the heart is responsible for pumping deoxygenated blood to the lungs, while the left side pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
The Chambers
Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cavae.
Right Ventricle: Pumps the deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins.
Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood to the body through the aorta, the largest artery in the body.
Valves of the Heart
The heart contains four main valves that ensure blood flows in the correct direction, preventing backflow:
Tricuspid Valve: Between the right atrium and right ventricle.
Pulmonary Valve: Between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery.
Mitral Valve: Between the left atrium and left ventricle.
Aortic Valve: Between the left ventricle and the aorta.
These valves open and close in response to pressure changes within the heart chambers, maintaining efficient blood flow.
The Heart’s Electrical System
Heart anatomy also includes the heart’s electrical system, which controls the heartbeat. The sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium, acts as the natural pacemaker, initiating electrical impulses. These impulses travel through the atria to the atrioventricular (AV) node, then through the bundle of His and Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract and pump blood.
Blood Supply to the Heart
The coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle itself. There are two main coronary arteries:
Left Coronary Artery (LCA): Divides into the left anterior descending artery and the circumflex artery, supplying the left side of the heart.
Right Coronary Artery (RCA): Supplies the right side of the heart.
Blockages in these arteries can lead to coronary artery disease, one of the leading causes of heart attacks.
Recent International Research on Heart Anatomy
International research has significantly advanced our understanding of heart anatomy and its complexities. For instance, studies have shown variations in heart anatomy across different populations, which can influence the prevalence and treatment of heart diseases.
Genetic Influences: Research from the European Heart Journal highlights how genetic factors can affect heart structure and function, leading to conditions like cardiomyopathy.
Technological Advances: A study published in The Lancet details how 3D imaging and other advanced technologies are providing unprecedented insights into heart anatomy, improving surgical outcomes and the design of medical devices.
Stem Cell Research: International collaborations, such as those reported in Nature, are exploring the use of stem cells to regenerate damaged heart tissue, offering hope for new treatments for heart disease.
Understanding heart anatomy is essential for both medical professionals and anyone interested in the science of the human body. The heart’s complex structure and function demonstrate the incredible adaptability and resilience of human physiology. As international research continues to uncover new details about heart anatomy, we can look forward to improved treatments and outcomes for heart disease, enhancing the quality of life for millions around the world.
Whether you are a student, a healthcare professional, or simply a curious reader, exploring the intricacies of heart anatomy offers valuable insights into the organ that sustains our very existence.



