Overview
Our body is made up of several important yet complex organs that work together as a system to provide smooth functioning for the human body. Out of those systems is the digestive system which consists of the Mouth, Pharynx, Esophagus also known as the food pipe, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. The rectum is a muscular tube about 13 cm long that is at the end of the large intestine. Sometimes, the blood vessels of the rectum and anus stretch so thin that the veins bulge and get irritated. The rectum connects the colon to the anus, which is the opening where waste products or stool exits the body.
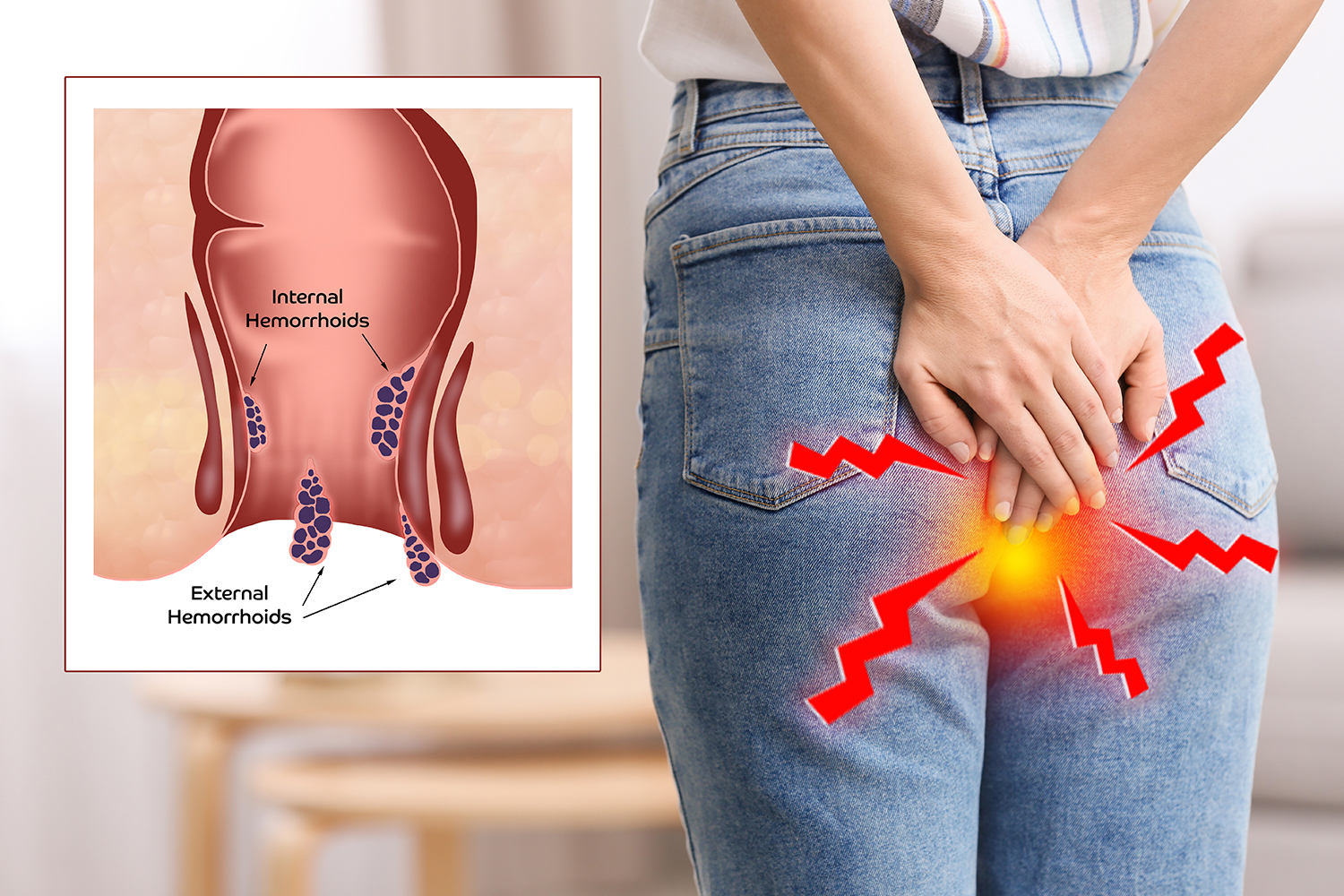
Hemorrhoids or piles are swollen veins in the lowest part of your rectum and anus. These swollen veins can cause pain, anal itching, and rectal bleeding. Excessive straining that increases the pressure on the belly or lower extremities can cause anal and rectal veins to become swollen and inflamed. Hemorrhoids may develop due to:
- Pelvic pressure from weight gain, especially during pregnancy.
- Pushing hard to have a bowel movement because of constipation.
- Straining to lift heavy objects or weightlifting.
Two types of hemorrhoids can grow on the anus and inside of the rectum which can be categorized as:
- External – Swollen veins form underneath the skin around the anus. External hemorrhoids can be itchy, painful, and sometimes they start to bleed. Occasionally, they bleed but sometimes they fill with blood that can clot which is not dangerous but can result in pain and swelling.
- Internal – Swollen veins from inside the rectum, which is a muscular tube that connects the anus with the large intestine. Internal hemorrhoids cannot be seen and felt but they might bleed, usually, internal hemorrhoids aren’t painful due to the less nerve-ending presence.
- Thrombosed Hemorrhoids – Clotting of blood in external hemorrhoids causes the color to change to purple or blue. One may notice symptoms like itching near the anus area opening, bleeding along with severe pain while passing the stool.
People can get symptomatic hemorrhoids if they:
- Are overweight or obese.
- Are pregnant.
- Have a low-fiber diet.
- Have chronic constipation or diarrhea.
- Regularly lift heavy objects.
- Spend a lot of time sitting on the toilet.
- Strain while having bowel movements.
A healthcare practitioner may recommend several tests to investigate and diagnose the category of hemorrhoids:
- Digital rectal exam – the health practitioner inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel for swollen veins.
- Anoscopy – this process requires a lighted tube also known as anoscope to view the lining of the anus and rectum.
- Sigmoidoscopy – in this process a lighted tube with a camera or also known as a sigmoidoscope is used to view inside the lower part of the colon and rectum.
What is the importance of Hemorrhoids Surgery Videos?
A healthcare specialist in normal functioning and disease diagnosis of the digestive system is known as a Gastroenterologist Surgeon. A Gastroenterologist surgeon is qualified to diagnose digestive system-related problems, perform or prescribe treatments. A gastroenterologist practitioner can help in developing strategies to treat illnesses, disorders, and issues related to the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. There are procedures available that help in shrinking or removing the hemorrhoids, such as using a laser. Although this might hurt a little and have fewer complications, surgery might be a better long-term choice, especially if the hemorrhoids are large and very painful or bleeding. Hemorrhoid surgery is safe and effective most of the time. But still, a fiber-rich diet is recommended to avoid constipation, and restrict activities that flare-up new hemorrhoids. There are several procedures that a healthcare practitioner can recommend:
- Hemorrhoidectomy – is a surgical procedure to remove hemorrhoids. After getting local or general anesthesia, the healthcare practitioner makes small cuts around the anus to slice the hemorrhoids away. Hemorrhoidectomy is often an outpatient procedure, and the patient can usually go home the same day. Due to the high sensitivity near the cuts stitches are done which can be tender and painful post-surgery. Recovery most often takes about 2 weeks.
- Procedure for Prolapse and Hemorrhoids (PPH) – also known as stapled hemorrhoidectomy, in this procedure the healthcare practitioner uses a stapler-like device to reposition the hemorrhoids and cut off the blood supply due to which the hemorrhoids eventually shrivel and die. It can treat hemorrhoids that have and have not prolapsed, or slipped down out of the anus. This procedure replaces hemorrhoids to the location where there are fewer nerve endings, which hurts less than a traditional hemorrhoidectomy.
- Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and Recto Anal Repair (HAL-RAR) – Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and Recto Anal Repair (HAL-RAR) is a new procedure in which a miniature Doppler sensor is inserted in the anus to detect the arteries supplying blood to hemorrhoids. The healthcare practitioner can pinpoint the arteries supplying the hemorrhoids and can tie them to cut off the blood supply. The hemorrhoids are reduced almost immediately and within weeks, hemorrhoids are no longer noticeable. The procedure is effective and virtually painless.



