Overview
Hip labral tear, a common yet often misunderstood injury, can significantly impact one’s quality of life and mobility. In recent years, extensive research has shed light on this condition, offering insights into its causes, symptoms, and effective treatment modalities. In this blog, we delve into the intricacies of hip labral tear, backed by facts and international research, to provide a comprehensive understanding of this orthopedic issue.
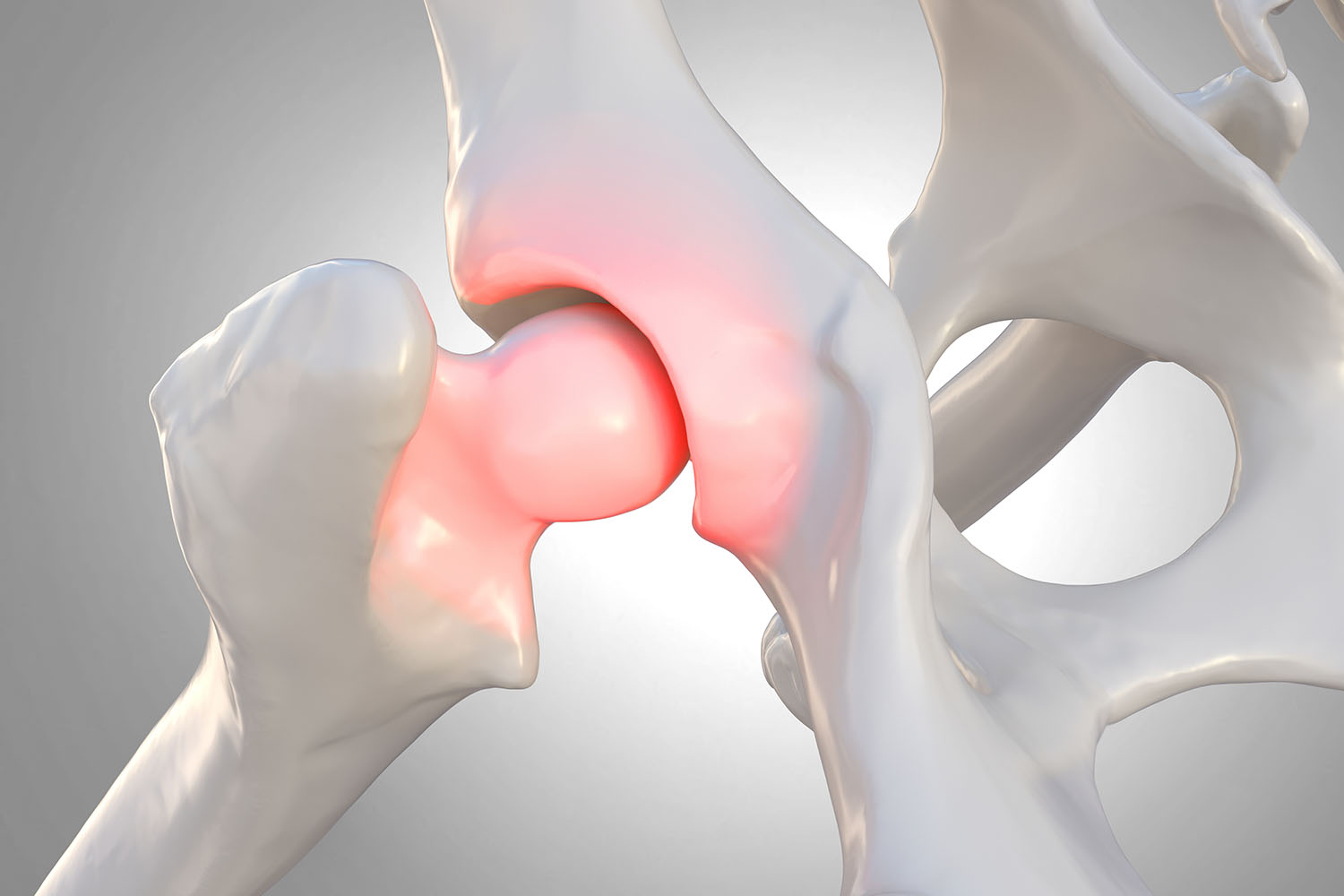
What is a Hip Labral Tear?
The hip labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the hip joint, providing stability and cushioning. A hip labral tear occurs when there is damage to this cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion in the hip joint. While the exact cause of hip labral tears can vary, they are commonly associated with repetitive motions, trauma, structural abnormalities, or degenerative changes in the hip joint.
Causes of Hip Labral Tear:
Research indicates several potential causes of hip labral tear, including:
Structural Abnormalities: Individuals with anatomical variations such as hip dysplasia or femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) are more prone to developing hip labral tears.
Trauma: Sudden trauma or injury, such as a fall or sports-related impact, can cause tears in the hip labrum.
Repetitive Movements: Activities that involve repetitive hip motions, such as running, dancing, or certain sports, may increase the risk of hip labral tears over time.
Degenerative Changes: Age-related degeneration of the hip joint can weaken the labrum, making it more susceptible to tears.
Symptoms of Hip Labral Tear:
Recognizing the symptoms of a hip labral tear is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
Hip Pain: Persistent pain in the groin area or deep within the hip joint is a hallmark symptom of hip labral tear.
Clicking or Catching Sensation: Some individuals may experience a clicking, locking, or catching sensation in the hip joint, particularly during movement.
Limited Range of Motion: A hip labral tear can lead to stiffness and decreased flexibility in the hip joint, affecting activities such as walking, bending, or squatting.
Instability: Feelings of hip joint instability or a sense of the hip giving way may occur in severe cases.
Treatment Options for Hip Labral Tear:
The management of hip labral tear typically involves a combination of conservative measures and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Treatment options may include:
Conservative Therapy: Non-surgical approaches such as rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and corticosteroid injections are often recommended to alleviate pain and improve hip joint function.
Arthroscopic Surgery: In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, arthroscopic surgery may be considered. During this minimally invasive procedure, the torn portion of the labrum is repaired or trimmed to restore hip joint stability.
Rehabilitation: Following surgery, a structured rehabilitation program is essential to facilitate recovery, strengthen the hip muscles, and improve range of motion.
Hip labral tear is a significant orthopedic condition that can affect individuals of all ages and activity levels. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options associated with hip labral tears, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively. With ongoing research and advancements in orthopedic care, the outlook for individuals with hip labral tears continues to improve, offering hope for a pain-free and active lifestyle.



