Overview
In the intricate tapestry of chronic pain management, one procedure stands out as a beacon of hope for those grappling with debilitating back pain: the medial branch block. This minimally invasive intervention offers targeted relief by disrupting pain signals originating from the facet joints of the spine. Let’s delve into the depths of the medial branch block, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and the research driving its efficacy.
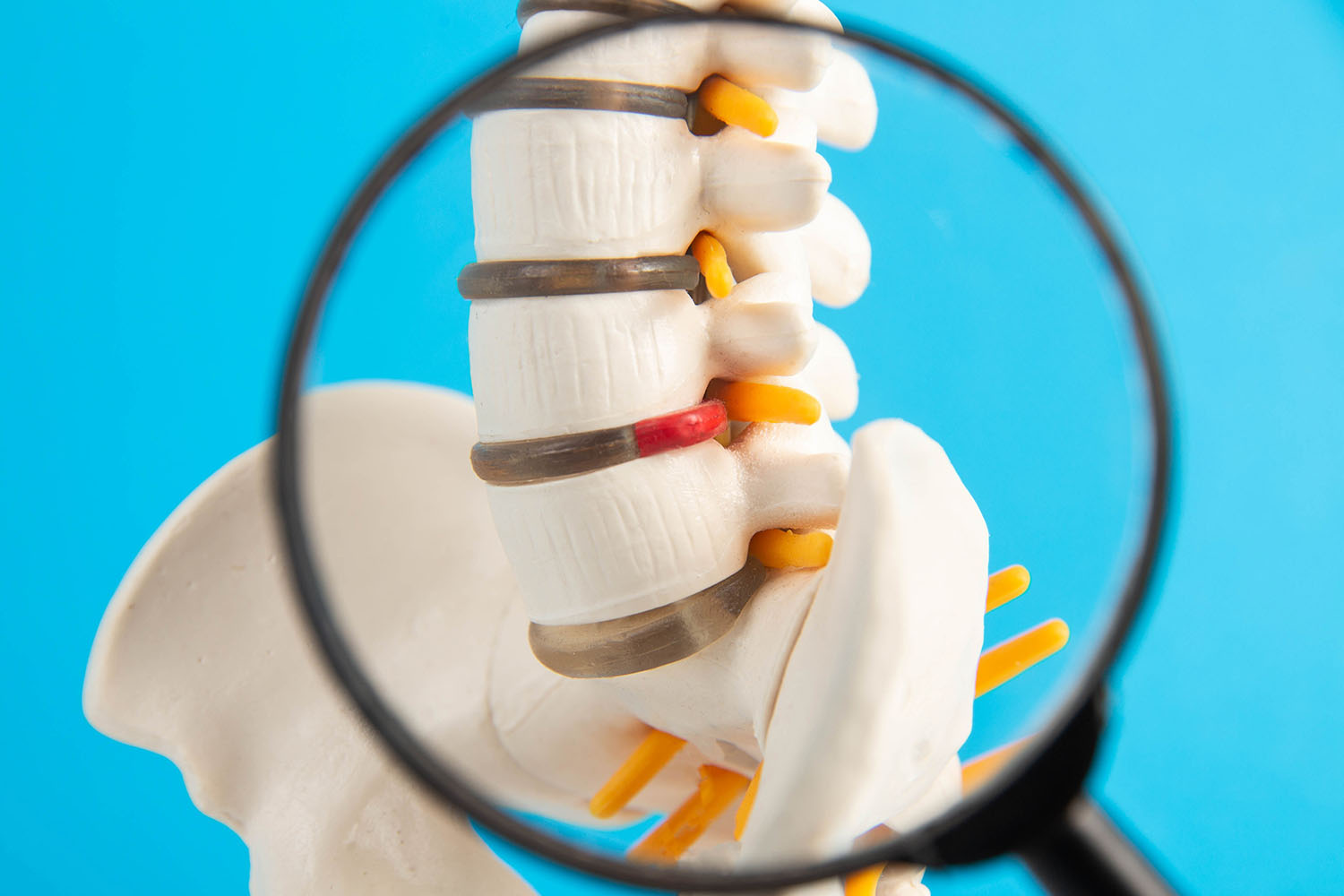
Medial branch block
Medial branch block : the very term evokes a sense of precision and relief, symbolizing a strategic approach to tackling persistent pain. But what exactly is a medial branch block, and how does it work? At its core, this procedure involves the precise injection of anesthetic medication near the medial branches of the spinal nerves that innervate the facet joints. By temporarily numbing these nerves, medial branch blocks effectively interrupt the transmission of pain signals, offering respite to individuals suffering from chronic back pain.
Research into medial branch blocks has yielded compelling evidence of their efficacy in providing short-term pain relief and facilitating the diagnosis of facet joint-related pain syndromes. Numerous studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain scores and improvements in functional outcomes following medial branch block procedures. Furthermore, research suggests that medial branch blocks can serve as valuable diagnostic tools, helping clinicians accurately pinpoint the source of a patient’s pain and tailor subsequent treatment strategies accordingly.
One notable area of research driving the evolution of the medial branch block lies in its application to various chronic pain conditions beyond traditional indications. Studies have explored the efficacy of medial branch blocks in treating conditions such as cervical facet joint pain, thoracic spine pain, and even headache disorders with cervicogenic origins. These findings underscore the versatility and potential of medial branch blocks as a valuable tool in the multidisciplinary management of chronic pain.
Moreover, advancements in imaging guidance techniques, such as fluoroscopy and ultrasound, have enhanced the accuracy and safety of medial branch block procedures, minimizing the risk of complications and optimizing patient outcomes. By precisely targeting the affected nerves, clinicians can deliver therapeutic interventions with unprecedented precision, maximizing the likelihood of successful pain relief.
Beyond its immediate analgesic effects, medial branch block offers additional benefits, including the potential to reduce reliance on opioid medications and improve overall quality of life for patients burdened by chronic pain. Furthermore, the minimally invasive nature of this procedure translates to shorter recovery times, minimal post-procedural discomfort, and the ability to resume normal activities shortly after treatment.
As we continue to unravel the complexities of chronic pain management, medial branch block emerges as a powerful tool in the arsenal of interventions aimed at alleviating suffering and restoring function. With ongoing research driving innovation and refinement, the future holds promise for further advancements in this field, offering renewed hope to individuals seeking relief from the burdens of chronic pain