Overview
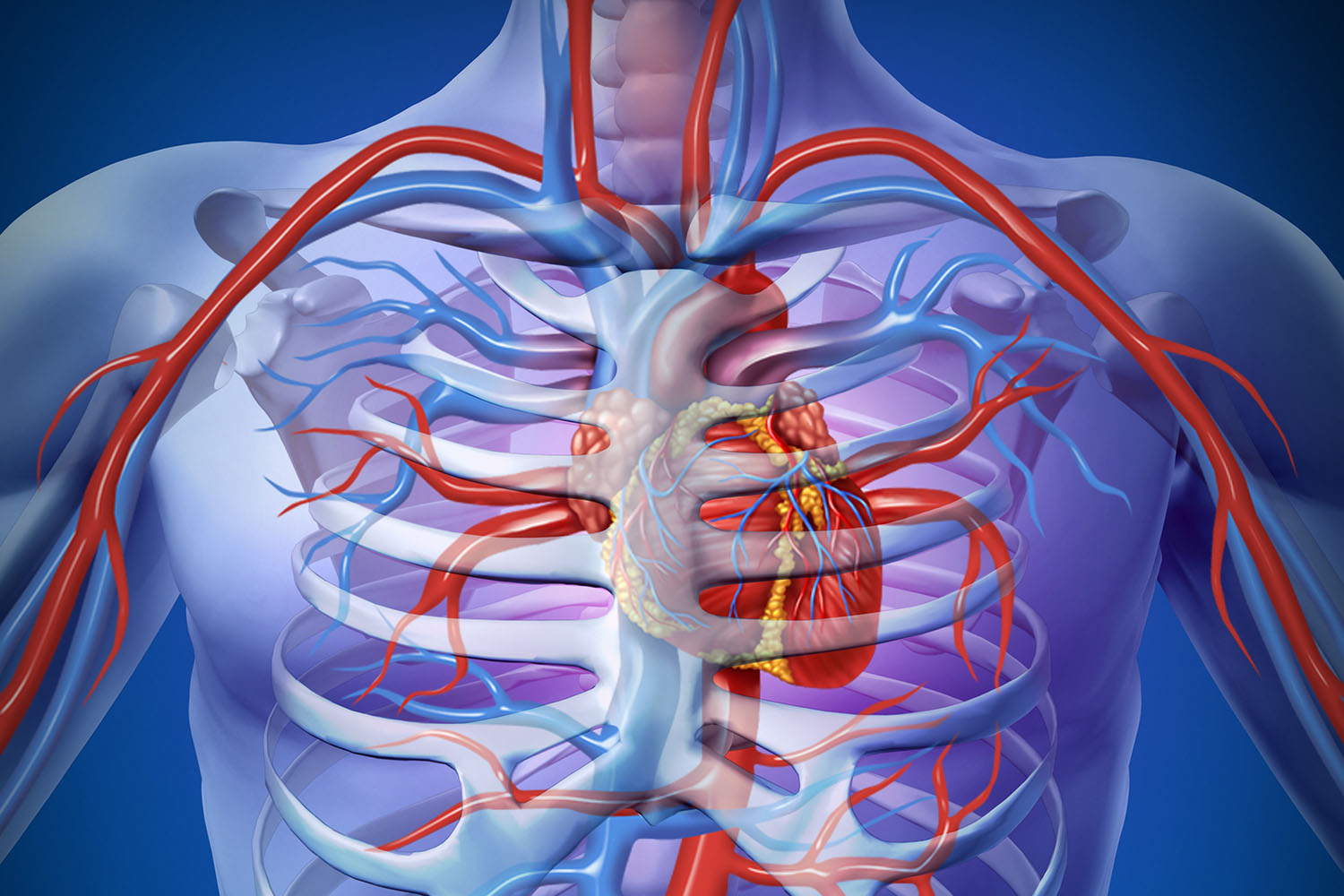
The human heart is not just a vital organ but also a symbol of life and emotion. Understanding its structure and function has been a central focus of medical research for centuries. Modern imaging technologies have provided an incredible picture of the heart in the human body, revealing its intricate details and offering insights that were once unimaginable.
A Glimpse into the Anatomy
The heart, a muscular organ roughly the size of a fist, is located slightly to the left of the center of the chest. It is encased in a protective sac called the pericardium and consists of four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. These chambers work in unison to pump oxygen-rich blood throughout the body and return oxygen-depleted blood to the lungs for reoxygenation.
Imaging Technologies: Creating the Picture of Heart in Human Body
Advancements in medical imaging have revolutionized our ability to visualize the heart. Techniques such as echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), and positron emission tomography (PET) provide detailed pictures of the heart in the human body. These images are crucial for diagnosing heart diseases, planning treatments, and conducting research.
- Echocardiography: This ultrasound-based technique uses sound waves to create real-time images of the heart. It is widely used for evaluating heart function, detecting structural abnormalities, and guiding interventional procedures.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI offers high-resolution images of the heart and surrounding structures without the use of ionizing radiation. It is particularly useful for assessing cardiac anatomy, tissue characterization, and blood flow dynamics.
- Computed Tomography (CT): CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the heart. This technology is essential for visualizing coronary arteries, detecting blockages, and planning surgeries.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): PET imaging involves the use of radioactive tracers to assess metabolic and functional processes in the heart. It is valuable for identifying areas of reduced blood flow and evaluating the viability of heart tissues.
International Research and Contributions
Global research initiatives have significantly enhanced our understanding of heart anatomy and diseases. Researchers worldwide utilize advanced imaging technologies to explore various aspects of cardiovascular health.
- United States: The Framingham Heart Study, initiated in 1948, has provided invaluable data on the epidemiology of cardiovascular diseases. This longitudinal study has led to the identification of numerous risk factors and contributed to the development of preventive strategies.
- Europe: The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) supports extensive research on cardiovascular diseases, emphasizing the importance of early detection and personalized treatment approaches. The EuroCMR Registry, for instance, collects data on cardiac MRI usage across Europe, helping to refine diagnostic and therapeutic techniques.
- Asia: In countries like Japan and China, large-scale studies focus on the genetic and environmental factors influencing heart health. The Hisayama Study in Japan has offered insights into the impact of lifestyle changes on cardiovascular outcomes over several decades.
The Future of Cardiac Imaging
The future holds exciting possibilities for cardiac imaging. Innovations like 3D printing, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning are set to further enhance the picture of the heart in the human body. These technologies promise to improve diagnostic accuracy, predict disease progression, and tailor treatments to individual patients.
The picture of the heart in the human body is a testament to the incredible advancements in medical science and technology. Through international research and collaboration, our understanding of the heart continues to evolve, paving the way for better cardiovascular health and improved patient outcomes.