Overview
Amidst the array of medical procedures aimed at safeguarding human health, polypectomy stands out as a crucial intervention in the realm of gastrointestinal care. Colon polyps, though often benign, can harbor the seeds of malignancy, making their timely removal imperative. Let’s embark on a journey through the realm of polypectomy, exploring the facts, research, and transformative impact of this procedure on colon health.
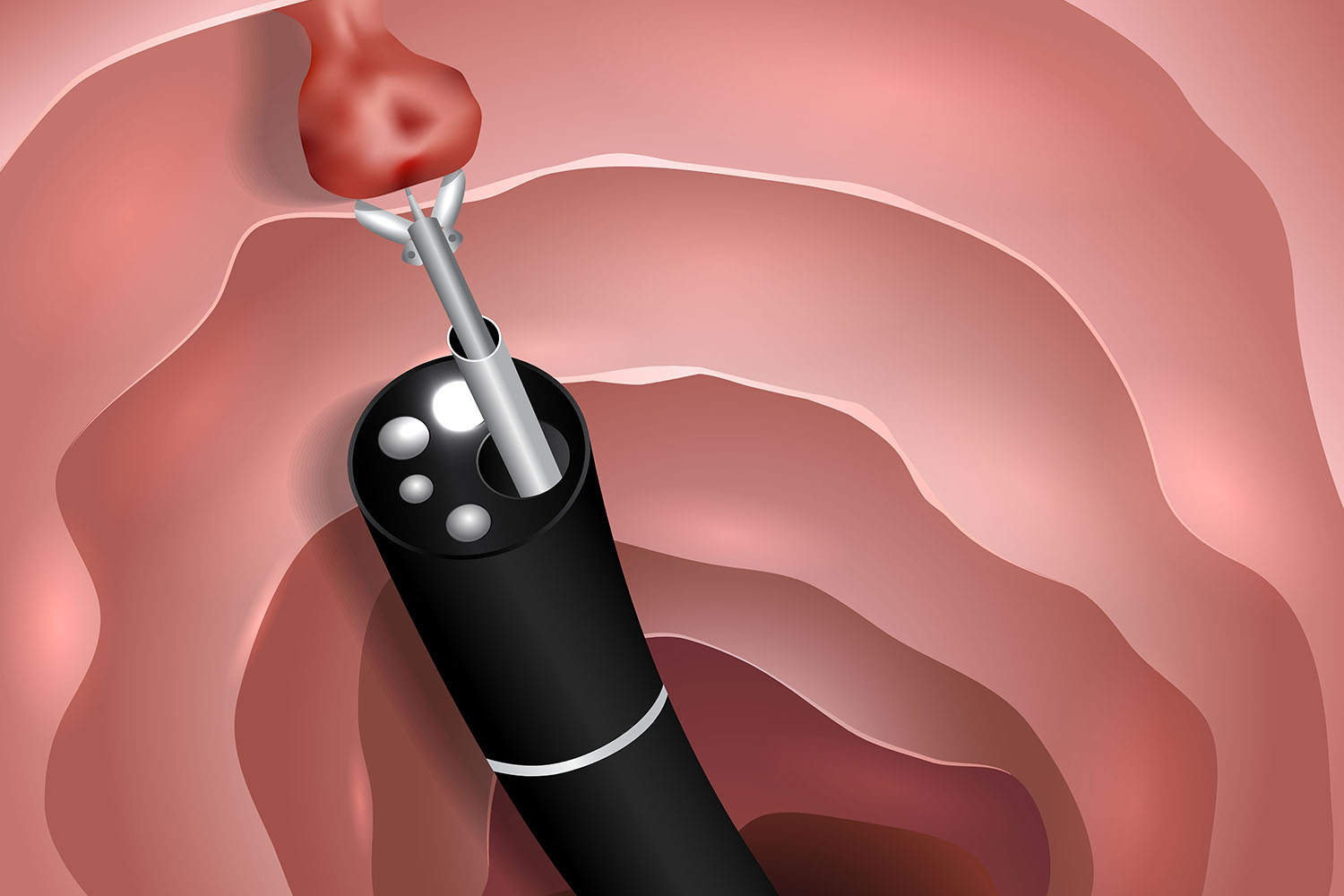
Understanding Polypectomy:
Polypectomy is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure designed to remove abnormal growths known as polyps from the colon lining. These polyps, which can range from small, benign growths to larger, potentially precancerous lesions, are detected through colonoscopies—a cornerstone of colorectal cancer screening. The timely removal of polyps via polypectomy not only alleviates symptoms but also mitigates the risk of colorectal cancer development.
Research Insights:
Decades of research have underscored the pivotal role of polypectomy in colorectal cancer prevention. A landmark study published in the New England Journal of Medicine demonstrated that the removal of adenomatous polyps during colonoscopy significantly reduces the incidence of colorectal cancer and related mortality. Furthermore, advancements in endoscopic imaging and polypectomy techniques have enhanced the detection and removal of even small, subtle polyps, further bolstering the efficacy of this procedure.
Identifying Candidates:
The decision to perform a polypectomy hinges on various factors, including the size, location, and histological characteristics of the polyp. While most polyps encountered during colonoscopy can be safely removed via polypectomy, certain complex or high-risk lesions may necessitate specialized interventions. A comprehensive evaluation by gastroenterologists and pathologists ensures precise risk stratification and tailored management strategies for each patient.
Surgical Techniques and Innovations:
Polypectomy techniques have evolved significantly over the years, with a focus on optimizing efficacy and minimizing procedural risks. Endoscopic modalities such as snare polypectomy, cold snare polypectomy, and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) offer versatile options for polyp removal, tailored to the individual characteristics of each lesion. Moreover, emerging technologies, such as advanced imaging and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), hold promise for enhancing the precision and efficiency of polypectomy procedures.
Postoperative Care and Surveillance:
Following polypectomy, meticulous postoperative care and surveillance are paramount to ensure optimal patient outcomes. Patients are typically advised to undergo periodic colonoscopic surveillance to monitor for polyp recurrence and detect new lesions. Research-backed surveillance guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations for post-polypectomy follow-up intervals, guiding clinicians in delivering personalized care and minimizing the risk of disease progression.
Long-Term Impact on Colon Health:
The enduring impact of polypectomy extends far beyond the immediate postoperative period, shaping the long-term landscape of colorectal health. Studies have consistently demonstrated the effectiveness of polypectomy in reducing the incidence of colorectal cancer and related mortality, underscoring its pivotal role in population-based screening programs. By facilitating the early detection and removal of precancerous lesions, polypectomy empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards preserving colon health and preventing colorectal cancer.
Polypectomy stands as a cornerstone of colorectal cancer prevention, offering a transformative solution for individuals at risk of colorectal neoplasia. Grounded in rigorous research and guided by technological innovations, this procedure epitomizes the convergence of science and medicine in the pursuit of optimal patient outcomes. As we navigate the complexities of colon health, let us recognize the profound impact of polypectomy in shaping a future free from the burden of colorectal disease.



