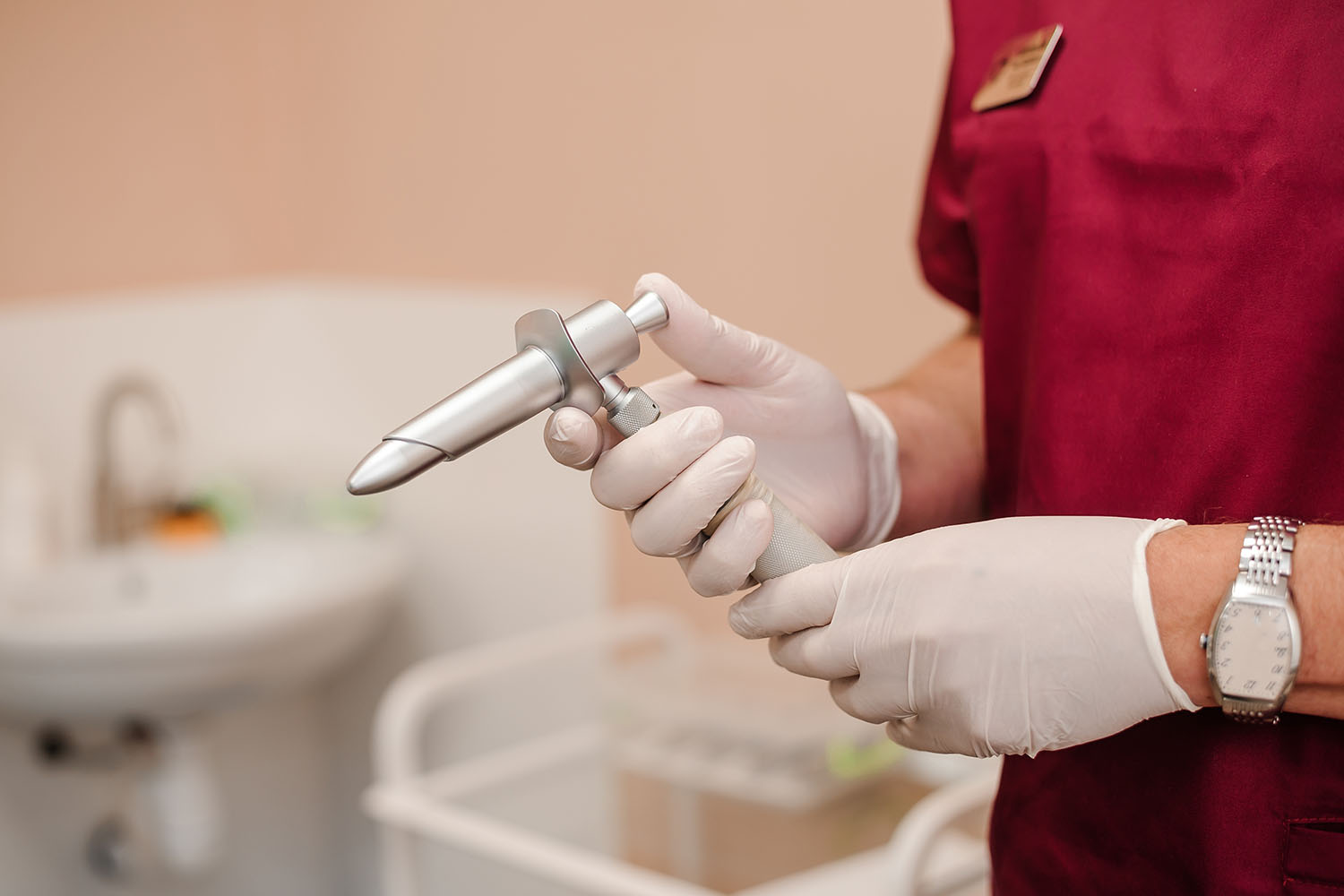
Overview
Proctoscope use is a critical component in the field of gastroenterology, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose and manage a variety of anorectal conditions. This device, a short, rigid tube equipped with a light source, offers direct visualization of the rectum and anal canal, making it an invaluable tool for both diagnosis and therapeutic interventions.
What is a Proctoscope?
A proctoscope is a medical instrument designed for examining the lower part of the rectum and the anal canal. Typically made of metal or plastic, it ranges in length from 7.5 to 15 cm and has a diameter of about 2.5 cm. Its primary function is to enable visual inspection, biopsies, and minor surgical procedures in the anorectal region.
The Importance of Proctoscope Use
Proctoscope use is crucial for several reasons:
- Diagnosis of Anorectal Diseases: Conditions such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, polyps, and rectal tumors can be effectively diagnosed through proctoscopy. The direct visualization provided by the proctoscope allows for accurate assessment and immediate diagnosis.
- Biopsies and Tissue Sampling: During a proctoscopic examination, physicians can take biopsies of suspicious lesions. This is vital for the early detection of malignancies and other pathological conditions.
- Therapeutic Interventions: Proctoscope use is not limited to diagnosis. It also facilitates therapeutic procedures such as sclerotherapy, banding of hemorrhoids, and the removal of polyps.
International Research on Proctoscope Use
International research underscores the significance of proctoscope use in improving patient outcomes. A study published in the International Journal of Colorectal Disease highlighted that proctoscopy is highly effective in the early detection of rectal carcinoma, particularly in high-risk populations . Another research article in the Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology emphasized that routine proctoscope use in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can help in early detection of complications like strictures and dysplasia .
Procedure and Patient Preparation
The procedure for proctoscope use is relatively straightforward but requires careful preparation:
- Patient Positioning: The patient is usually positioned in the left lateral decubitus (left side lying) position or the lithotomy position. This positioning provides optimal access to the rectum and anus.
- Lubrication: To minimize discomfort, the proctoscope is lubricated before insertion.
- Insertion and Examination: The proctoscope is gently inserted into the anal canal and advanced into the rectum. The healthcare provider then inspects the area for abnormalities.
- Biopsy or Treatment: If necessary, the provider can take biopsies or perform minor procedures during the examination.
Safety and Comfort
Patient comfort and safety are paramount during proctoscope use. Though the procedure might cause some discomfort, it is generally well-tolerated. Local anesthetics or sedation can be used for patients who are particularly anxious or sensitive.
Advances in Proctoscope Technology
Advances in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated proctoscopes with features such as enhanced lighting, magnification, and video capabilities. These advancements improve diagnostic accuracy and patient comfort.
Proctoscope use remains a cornerstone in the diagnostic and therapeutic arsenal of gastroenterology. With ongoing research and technological advancements, its effectiveness and patient comfort continue to improve. By facilitating early detection and treatment of anorectal conditions, proctoscope use plays a crucial role in enhancing patient outcomes and advancing the field of gastrointestinal health.
As research progresses and more refined techniques are developed, the future of proctoscope use looks promising, heralding even more precise and less invasive methods for managing anorectal health