Overview
Skin hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts that appear on the skin’s surface. These red, pink, or sometimes skin-colored bumps can be quite bothersome, causing significant discomfort. While most people experience skin hives at some point in their lives, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can be empowering.
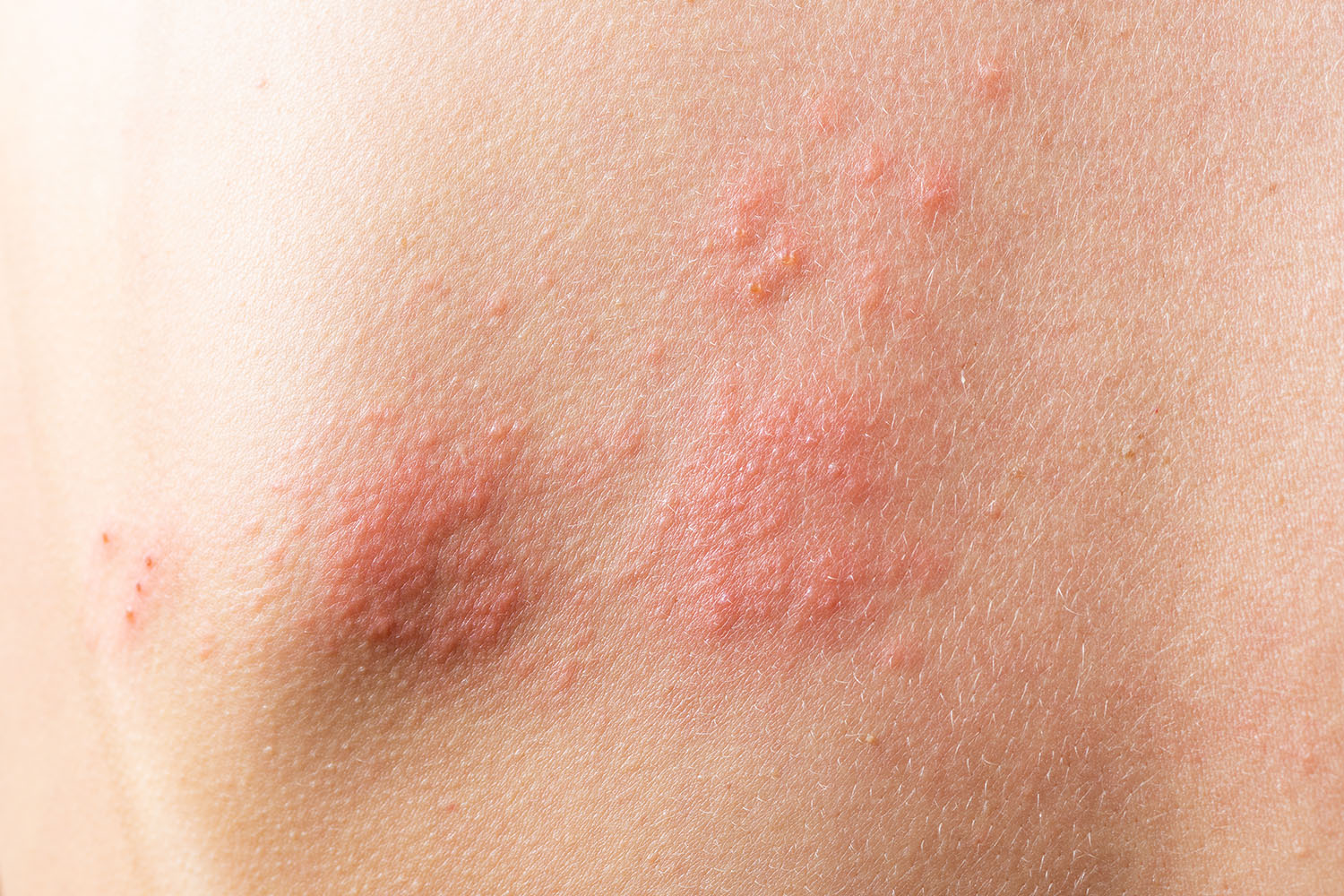
What Causes Skin Hives?
The culprit behind skin hives is often an allergic reaction. When your immune system encounters a foreign substance it perceives as a threat (an allergen), it releases chemicals like histamine. This release triggers inflammation, leading to the characteristic welts and itching associated with skin hives.
Some common triggers of skin hives:
Food allergies: Certain foods, particularly peanuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy, are frequent triggers of skin hives, especially in children.
Medication allergies: Medications like penicillin, aspirin, and ibuprofen can also cause skin hives as an allergic reaction.
Insect bites or stings: The body’s response to insect bites or stings can sometimes manifest as skin hives.
Physical factors: Pressure on the skin from tight clothing, friction, or even exposure to extreme temperatures (hot or cold) can induce skin hives.
Underlying medical conditions: In some cases, skin hives can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as thyroid problems, autoimmune diseases, or infections.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Skin Hives
The telltale signs of skin hives are often unmistakable:
- Raised, itchy welts that can vary in size and shape.
- The welts may appear red, pink, or skin-colored, depending on your skin tone.
- The welts typically come and go quickly, disappearing within hours and recurring in different areas.
- In some cases, skin hives may be accompanied by swelling of deeper skin layers, known as angioedema.
It’s important to note that skin hives can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting more than six weeks). If your skin hives persist for an extended period, consulting a doctor is crucial to identify the underlying cause.
Soothing the Itch: Treatment Options for Skin Hives
The good news is that several treatment options can help alleviate the discomfort of skin hives.
Antihistamines: These medications block the action of histamine, the chemical responsible for itching and inflammation. Over-the-counter antihistamines are often the first line of defense for mild skin hives.
Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroids applied directly to the skin can reduce inflammation and itching associated with skin hives. Oral corticosteroids may be prescribed in severe cases.
Identifying and avoiding triggers: If a specific allergen triggers your skin hives, avoiding that substance can significantly reduce flare-ups. Keeping a journal to track potential triggers can be helpful.
When to See a Doctor About Skin Hives
While most cases of skin hives are harmless and resolve on their own, seeking medical attention is essential in certain situations:
- f your skin hives are accompanied by severe swelling, particularly around the face, lips, or throat.
- If you experience difficulty breathing or wheezing.
- If your skin hives are accompanied by fever, nausea, or vomiting.
- If your skin hives persist for more than six weeks (chronic hives).
By understanding the causes and symptoms of skin hives and knowing when to seek medical help, you can manage this condition effectively and find relief from the bothersome itch.



